13 Types Of Adjectives And How To Use Them
Adjectives are one of the most exciting parts of speech that we have. Without adjectives, you wouldn’t be able to tell your friends which movies are great and which are overrated. Adjectives also allow us to describe ourselves as being amazing, incredible, fantastic, and—of course—humble. Most importantly, adjectives let us explain the difference between funny memes and bad ones.
Based on these indisputable facts, adjectives are clearly important parts of grammar. But did you know that there are many different types of adjectives? It’s true! In fact, there are at least 13—yes, 13!—types of adjectives that we commonly use.
What is an adjective?
An adjective is a word that modifies a noun or a pronoun. In general, adjectives usually give us more information about a noun or pronoun by describing it or providing more information about it. For example, the adjective funny is used to say something causes fun or laughter.
We are going to look at types of adjectives that we commonly use in everyday writing and speech. Before we do, though, there are a couple things we need to address first.
Mục lục
Cumulative and coordinate adjectives
These two terms for adjectives have more to do with good writing practices than grammatical concepts. The terms cumulative adjectives and coordinate adjectives are often used in guides or advice covering writing, proper adjective order, or punctuation. The term coordinate adjectives is used to refer to adjectives that can be written in any order and are usually separated by a comma or the word and. For example, the words heavy and huge are the coordinate adjectives in the sentence He was carrying a huge, heavy stone. The term cumulative adjectives is used to refer to adjectives that fall under different categories, often don’t use commas, and follow adjective order as in the adjectives used in the sentence He was a young French man.
Determiners
Unlike nouns and verbs, the types of adjectives are not as strictly defined. For this reason, style guides and grammar resources may not consider some of the types of adjectives you are about to learn about to actually be adjectives at all. In particular, a style guide may consider words that act as possessives, demonstratives, interrogatives, and quantifiers to either be their own parts of speech or a type of word known as determiners, which also often includes articles. While we will treat these words as adjectives, you shouldn’t be surprised if you see them referred to as a different part of speech.

Common types of adjectives
We are going to briefly examine 13 different types of adjectives. If you’d like to learn about each type of adjective in more detail, you can check out all of our amazing guides to the different kinds of adjectives!
- Comparative adjectives
- Superlative adjectives
- Predicate adjectives
- Compound adjectives
- Possessive adjectives
- Demonstrative adjectives
- Proper adjectives
- Participial adjectives
- Limiting adjectives
- Descriptive adjectives
- Interrogative adjectives
- Attributive adjectives
- Distributive adjectives
After you’ve reviewed the adjectives here (or if you’re already an adjective expert), take this quiz to see how much you’ve learned!
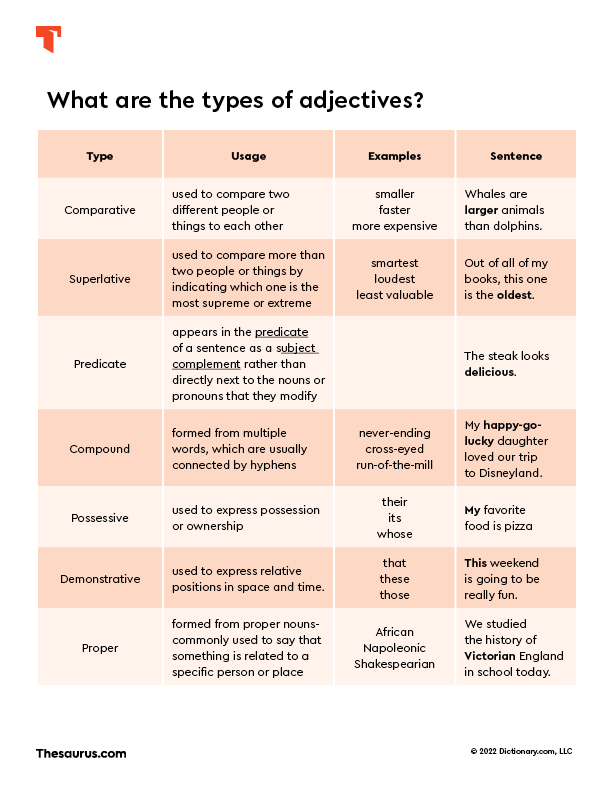
1. Comparative adjectives
Comparative adjectives are used to compare two different people or things to each other. Some examples of comparative adjectives include words such as smaller, faster, more expensive, and less reasonable.
Comparative adjective examples
- Whales are larger animals than dolphins.
- We moved to a cheaper apartment.
- The sequel was even more incredible than the first movie.
2. Superlative adjectives
Superlative adjectives are used to compare more than two people or things by indicating which one is the most supreme or extreme. Some examples of superlative adjectives include words such as smartest, loudest, most impressive, and least valuable.
Superlative adjective examples
- Adrian is the fastest member of our team.
- Out of all of my books, this one is the oldest.
- We are trying to figure out the least confusing way to explain the lesson to the new students.
3. Predicate adjectives
Predicate adjectives are adjectives that appear in the predicate of a sentence as a subject complement rather than directly next to the nouns or pronouns that they modify. Predicate adjectives follow linking verbs in sentences and clauses.
Predicate adjective examples
- Andrea is tall.
- Freddy became angry.
- The steak looks delicious.
Understand the difference between subjects and predicates here.
4. Compound adjectives
Compound adjectives are adjectives that are formed from multiple words, which are usually connected by hyphens. Some examples of compound adjectives include never-ending, cross-eyed, and run-of-the-mill.
Compound adjective examples
- She had enough of the double-dealing salesman.
- My happy-go-lucky daughter loved our trip to Disneyland.
- The better-off members of the city live by the river.
5. Possessive adjectives
Possessive adjectives are often used to express possession or ownership. The most commonly used possessive adjectives are my, your, its, her, his, our, their, and whose.
Possessive adjective examples
- My favorite food is pizza.
- Sydney spent the day with her parents.
- Canadians celebrated their team’s victory at the Olympics.
6. Demonstrative adjectives
Demonstrative adjectives are used to express relative positions in space and time. The most commonly used demonstrative adjectives are this, that, these, and those.
Demonstrative adjective examples
- This watch is cheaper than that one.
- This weekend is going to be really fun.
- Watch out for those prickly rose bushes next to you.
7. Proper adjectives
Proper adjectives are adjectives formed from proper nouns. In general, proper adjectives are commonly used to say that something is related to a specific person or place. Proper adjectives include words such as African, Napoleonic, and Shakespearian.
Proper adjective examples
- He was reading a Russian newspaper.
- I think Haitian food is tasty.
- We studied the history of Victorian England in school today.
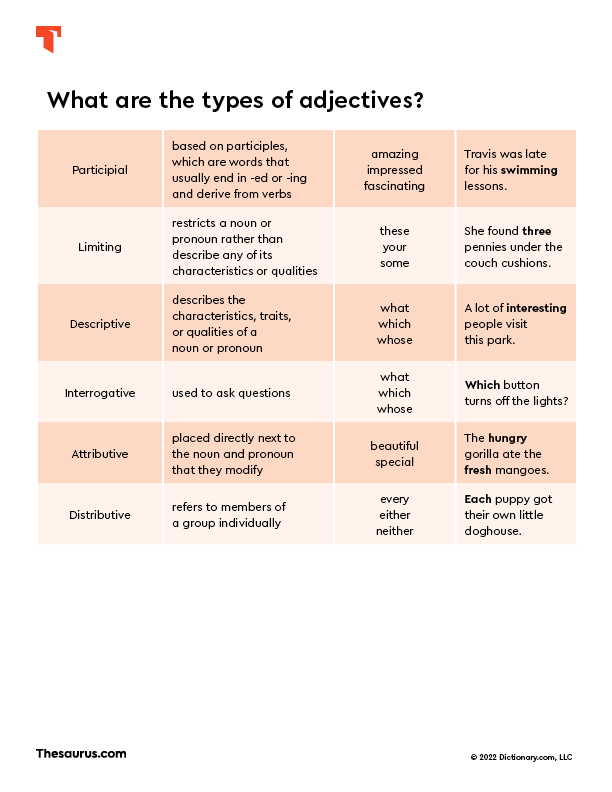
8. Participial adjectives
Participial adjectives are adjectives that are based on participles, which are words that usually end in -ed or -ing and derive from verbs. Participial adjectives include words like amazing, impressed, and fascinating.
Participial adjective examples
- Travis was late for his swimming lessons.
- Please hand me my reading glasses.
- The silly clown cheered up the bored children.
Take part in this discussion on the forms and uses of participles if you want to learn more.
9. Limiting adjectives
Limiting adjectives are adjectives that restrict a noun or pronoun rather than describe any of its characteristics or qualities. Limiting adjectives overlap with other types of adjectives such as demonstrative adjectives and possessive adjectives. Limiting adjectives include words such as these, your, and some.
Limiting adjective examples
- I bought some eggs at the store.
- She found three pennies under the couch cushions.
- Take a look at that house over there.
10. Descriptive adjectives
Descriptive adjectives are adjectives that describe the characteristics, traits, or qualities of a noun or pronoun. Most adjectives are descriptive adjectives. Words such as purple, friendly, and attractive are examples of descriptive adjectives.
Descriptive adjective examples
- A lot of interesting people visit this park.
- She told a scary story.
- The leaves turned orange and red.
11. Interrogative adjectives
Interrogative adjectives are adjectives that are used to ask questions. The interrogative adjectives are what, which, and whose.
Interrogative adjective examples
- What color is your favorite?
- Which button turns off the lights?
- Whose turn is it to wash the cat?
12. Attributive adjectives
Attributive adjectives are adjectives that are directly next to the noun and pronoun that they modify. Usually, attributive adjectives come directly before nouns and pronouns but they modify. But they can sometimes appear after them.
Attributive adjective examples
- She has beautiful handwriting.
- The hungry gorilla ate the fresh mangoes.
- Keith gave his dad something special for his birthday.
13. Distributive adjectives
Distributive adjectives are used to refer to members of a group individually. Examples of distributive adjectives include each, every, either, and neither.
Distributive adjective examples
- Each puppy got their own little doghouse.
- Every member of the team scored a goal.
- I’ll be happy if either candidate wins the election.
Demonstrate your adjective skills by taking this quiz!
All the adjectives, none of the errors
You won’t mistake your adjectives again when you check your writing on Thesaurus.com’s Grammar Coach™. This writing tool uses machine learning technology uniquely designed to catch grammar and spelling errors. Its Synonym Swap will find the best nouns, adjectives, and more to help say what you really mean, guiding you toward clearer, stronger, writing.
Whether you’re using proper, limiting, or descriptive adjectives, start writing smarter today!






