Fault Tree Analysis
What is Fault Tree Analysis
Fault tree analysis (FTA) is a graphical tool used to explore the causes of system-level failures. It uses Boolean logic to combine a series of lower-level events. It is basically a top-down approach to identify the component-level failures (basic events) that cause the system-level failures (top events). Fault tree analysis consists of “events” and “logic gates,” which connect the events to identify the cause of the top undesired event.
Fault tree analysis is easier than the Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA) as it focuses on all possible system failures of an undesired top event. At the same time, FMEA conducts analysis to find all possible system failure modes irrespective of their severity.
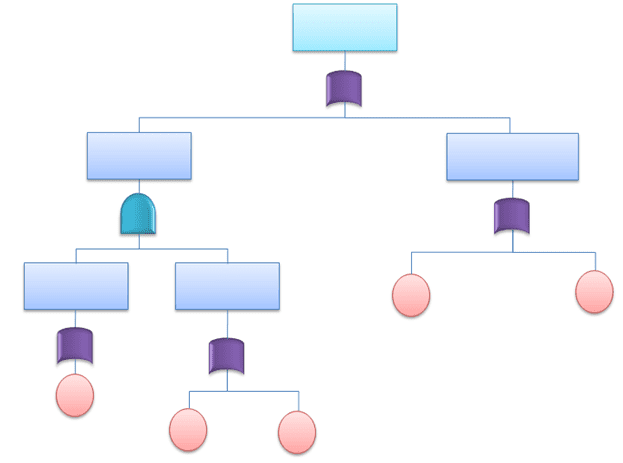 FTA Diagram
FTA Diagram
History of Fault Tree Analysis
Fault tree analysis is a top-down approach originally developed in Bell laboratories by H Watson and A Mearns for the air force in 1962. This concept was later adopted by Boeing, and today, it is widely used in the aerospace, automobile, chemical, nuclear, and software industries, especially for reliability and safety events.
When Would You Use FTA
Fault tree analysis can be used to perform all types of system-level risk assessment processes. The purpose of FTA is to effectively identify the cause(s) of system failure and mitigate the risks before it occurs. This is an invaluable tool for complex systems that visually displays the logical identification of the problem. Moreover, system efficiency can be attained by this analysis. It can be implemented alone or complement Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA).
FTA Symbols
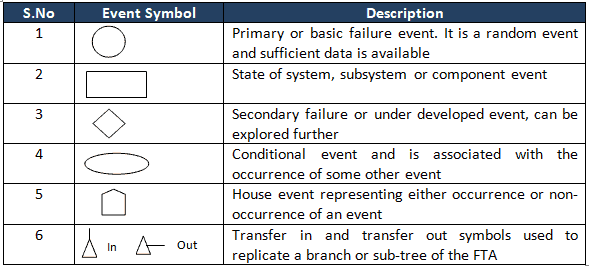
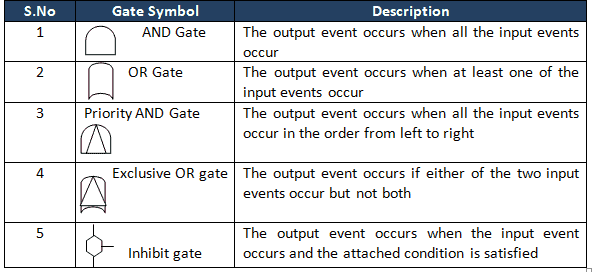
A Fault Tree uses logical gates to perform an analysis. There are numerous FTA symbols exist, but these are broadly divided into two categories: Event symbols and Gate symbols.
Event Symbols in FTA
Gate Symbols in FTA
How do you do Fault Tree Analysis
- Define the primary failure to be analyzed. In other words, identify the undesirable top event.
- Identify first-level contributors who are just below the top level using the available technical information.
- Link these contributors to the top-level event by using logical gates (AND, OR gates), and also see the relationship so that it will help to identify the appropriate logical gate.
- Identify the second-level contributors and link to the top by using logical gates.
- Identify the minimal cut set.
- Repeat the same steps till the basic causes,
- Finally, complete and evaluate the FTA.
- Calculate the probability of lowest level elements occurrence and also measure the probabilities from the bottom up.
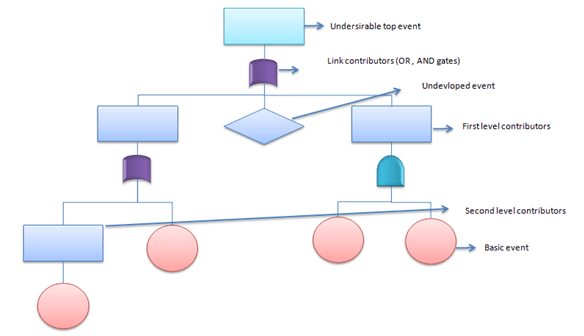
Minimal Cut Sets
One of the important factors in the qualitative analysis of fault trees is to identify a minimal cut set. For instance, complex and large fault trees have to use superior tools (algorithms for extraction) to get the minimal cut sets.
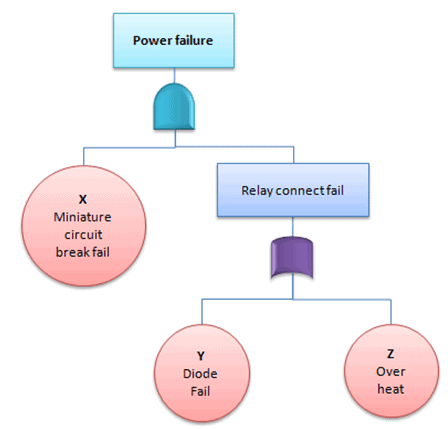
Cut set: A set of
basic events that together cause the TOP undesirable event.
Ex: X, Y, and Z (from the below picture)
Minimal cut set: A cut set with a minimal number of events that can still cause the TOP undesirable event. In other words, the TOP undesirable event occurs if one or more minimal cut set occurs.
Ex: (X and Y); (X and Z) from the below picture
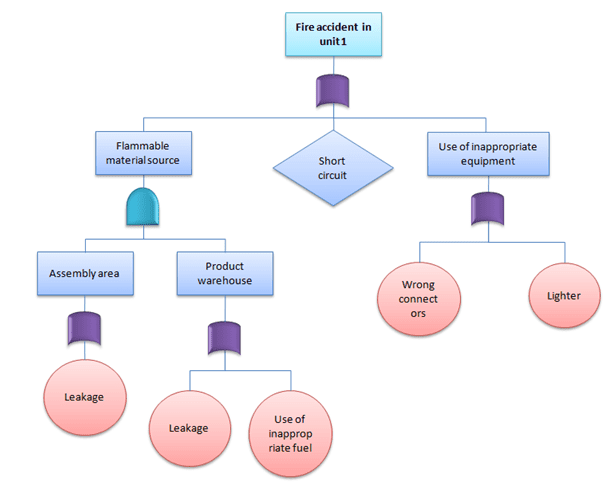
Practical Example of FTA
A fire broke out at unit 1 of XYZ cable manufacturing company despite the safety system in place. General Manager was very concerned about the accident and requested the Safety Officer in charge to evaluate the system. However, as part of the initial analysis of the existing system, the safety team used FTA to identify the different causes of the accident.
Quantitative Fault Tree Analysis
The top undesirable event occurs if one or more of the minimal cut sets occurs. Hence, the main target is to identify minimal cut sets. Moreover, if all the minimal cuts are independent of each other, then we could compute the probability of the top undesirable event by:
![]()
Where Pj is the failure probability of the minimal cut set
Example: Find the
probability of water pump failure from the below example
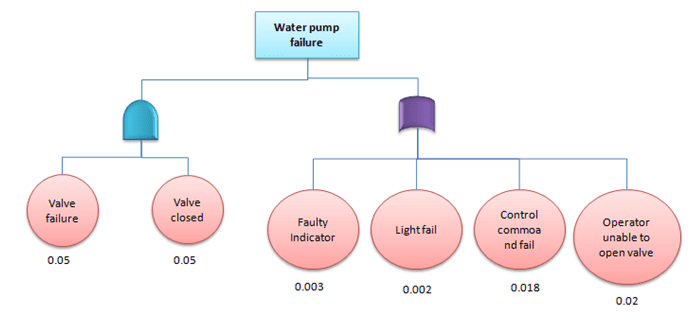
The water pump will fail because of value failure and value closed or fault indicator or light failure or control command failure or operator unable to open the valve, since OR gates add and AND gates multiply the probability of pump failure
μpumpfail =1-(0.05*0.05)*(1-0.003)*(1-0.002)*(1-0.018)*(1-0.02)
= 0.0448
Hence, the probability of water pump failure = 4.48%
Advantages of Fault tree analysis
- The fault tree visually depicts the analysis that will help the team to work on the cause of an event in a logical way that leads to failure.
- Highlights the critical components related to system failure.
- Provides an efficient method to analyze the system.
- Unlike other analysis methods, human errors are also included in the analysis.
- It helps to prioritize the action items to solve the problem.
- Provides qualitative and quantitative analysis.
Disadvantages of Fault tree analysis
- Too many gates and events to be considered for large system analysis.
- The basic disadvantage is that it examines only one top event.
- Common cause failures are not always obvious.
- Difficult to capture time-related and other delay factors.
- Needs experienced individuals to understand the logical gates.
Helpful Videos






