Flowchart as an Integral Component of Seven Basic Quality Tools
Flowchart in the context of seven basic quality tools is defined as to describe the graphical presentation of a process.
A process can be viewed as a sequence of activities performed collectively to achieve specific objectives. These sequences of activities include set of inputs, decision branch nodes and resultant output. A flowchart can be used to visualize the sequence of events of a process either performed sequentially or in parallel.
As per thePMBOK® Guide Flowcart is
The depiction in a picture format of the input, process actions, and outputs of one or more methods within a System.
Flowchart Example: For instance, if team wants to estimate items identified in the scope baseline, then there are certain steps iteratively to derive at realistic estimates.
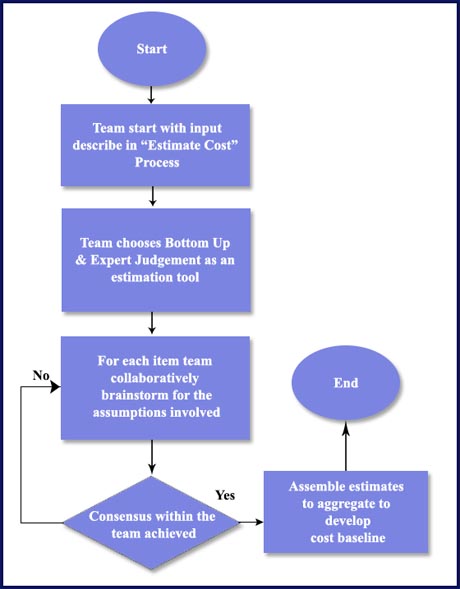
Development of Flowchart-A Flowchart is developed after establishing the understandings of inputs, output, decision points and basis of decisions. Many professionals use SIPOC as an input to develop a visual representation of a process.
Here SIPOC (Supplier, Input Process, Output and Customer) is a model to document a process from beginning to end, where team members are agreed for the process sequences after summarizing all the input and output.
SIPOC is a result of brainstorming session between selected group of team members and other SME(s). In order to develop SIPOC model team starts with ‘P’ of SIPOC for the steps of processes. After identification of the process steps, list of output and customers are identified. The team continues from backward of SIPOC i.e. beginning with the supplier (S) first and then inputs of the processes are identified.
The result of SIPOC is generally represented in table as mentioned below; here numbers are allotted to each head of the table according to their sequence of consideration:






