The Four Cs of Diamonds | Diamond Color and Clarity Scale
While this page is here to help you learn about the 4 C’s of diamonds, we are also available to help you directly. Our staff GIA Graduate Gemologists are here to help you at every stage of your process – whether you are looking to buy today or in six months.
Mục lục
Diamond Cut
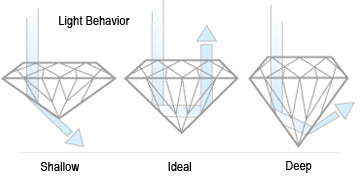 Although terms like “princess cut” and “cushion cut” are often used to describe diamonds, these are actually references to the diamond’s shape. , in the case of the 4 Cs of diamonds, refers to proper angling of a diamond’s to ideally reflect light and bring brilliance to the stone. Because light and sparkle are the most important parts of a diamond’s appearance, this is the most important of the 4 Cs of diamonds. According to the four Cs of diamonds chart, a good diamond that is badly cut is essentially ruined, while a less valuable diamond cut extremely well can become more attractive and valuable. Review our diamond color and clarity scale to choose the right diamond.
Although terms like “princess cut” and “cushion cut” are often used to describe diamonds, these are actually references to the diamond’s shape. , in the case of the 4 Cs of diamonds, refers to proper angling of a diamond’s to ideally reflect light and bring brilliance to the stone. Because light and sparkle are the most important parts of a diamond’s appearance, this is the most important of the 4 Cs of diamonds. According to the four Cs of diamonds chart, a good diamond that is badly cut is essentially ruined, while a less valuable diamond cut extremely well can become more attractive and valuable. Review our diamond color and clarity scale to choose the right diamond.
Diamond Color
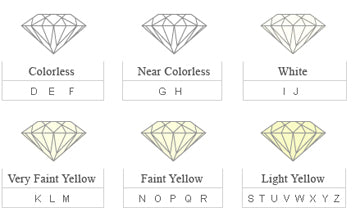 Diamonds are graded on a scale from D-Z. Because of our high standards, deBebians sells only diamonds graded from D-J. On the diamond clarity scale, there are certain ranges within the GIA color grading scale. For example, a diamond graded D-F is considered to be colorless. Diamonds graded from G-H are considered to be near colorless.
Diamonds are graded on a scale from D-Z. Because of our high standards, deBebians sells only diamonds graded from D-J. On the diamond clarity scale, there are certain ranges within the GIA color grading scale. For example, a diamond graded D-F is considered to be colorless. Diamonds graded from G-H are considered to be near colorless.
Generally speaking, the naked eye cannot tell the difference between one or two color grades on a loose diamond. Once a diamond is mounted into a setting the eye cannot tell the difference between three color grades. This means you can buy a F, G, or H color diamond and not really be able to detect much of a difference.
The body color of a diamond is one of the 4 C’s that is detectable with the naked eye. A colorless diamond is colorless due to its ability to absorb rays of light equally. These diamonds are rare and expensive. Diamonds that are in the D-F range are considered colorless and carry a higher premium. Diamonds in the G-J range will face-up white and are sometimes a much better value than colorless diamonds. Diamonds that are K color or below will face-up with a slight hint of yellow.
and its impact on diamond color: Fluorescence is a naturally occurring phenomenon in diamonds and it usually masks the overall body color of a diamond. Fluorescence is graded on a scale of none, faint, medium, strong and very strong. Generally fluorescence will mask the body color of a diamond to make the stone appear whiter. In other words, if you are seeking a diamond of a slightly lower color grade, looking for one with some fluorescence will make the diamond appear whiter.
Diamond Clarity
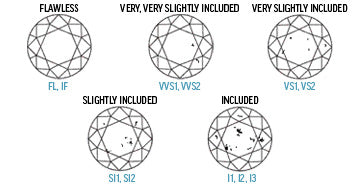 Most diamonds have inclusions. Therefore diamonds are graded on a scale from flawless (FL) to included (I3) to set them apart from one another. The less inclusions a diamond has, the rarer that particular diamond is, and the more valuable it is. deBebians sells only diamonds from IF to SI2. GIA and AGS have set standards for what classifies a diamond to have a particular grade. Please review our clarity chart for diamonds below that will better help explain each diamond grade’s typical characteristics.
Most diamonds have inclusions. Therefore diamonds are graded on a scale from flawless (FL) to included (I3) to set them apart from one another. The less inclusions a diamond has, the rarer that particular diamond is, and the more valuable it is. deBebians sells only diamonds from IF to SI2. GIA and AGS have set standards for what classifies a diamond to have a particular grade. Please review our clarity chart for diamonds below that will better help explain each diamond grade’s typical characteristics.
FL/IF
Flawless or internally flawless. These diamonds have no inclusions and are extremely rare!
VVS1/VVS2
Very, very slightly included. These diamonds require a 60x magnification to clearly see inclusions. The inclusions in these diamonds are hard for even a trained grader to see under 10x magnification.
VS1/VS2
Very slightly included. These diamonds require 30x magnification to clearly see inclusions. These diamonds will be eye-clean. Compare these diamond prices to those in the VVS category and you’ll probably see that these offer a really good value.
SI1/SI2
Slightly included. Generally requires 10x magnification to clearly see inclusions. Sometimes larger SI diamonds are not completely eye clean. Feel free to call us and our GIA Graduate Gemologists can examine SI diamonds to see if they are eye-clean. SI diamonds offer some of the best values.
I1/I2/I3
Included. These diamonds will more than likely have eye-visible inclusions. deBebians does not sell loose diamonds in these grades.
A good way to determine what clarity grade to select is to consider your budget. We recommend diamonds that are eye-clean — meaning you cannot see any of the inclusions by just looking at the diamond. This will include diamonds from IF usually down to the SI category. Please call us if you have any questions regarding a clarity grade. Our expert GIA Graduate Gemologists will be able to guide you in your search for that perfect diamond you are seeking.
Diamond Carat Weight
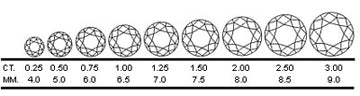 weight is probably the easiest of the 4 C’s to understand. Diamond weight is measured in carats. There are 100 points in 1 carat (or 1 ct., when abbreviated). This means that a three quarter carat diamond can be referred to as “a 75-pointer” or “75 points”. Keep in mind that carat weight is only a measure of weight but not necessarily size (i.e. its measurements or the size it shows when facing up). The actual cut of a diamond will play a big role in the overall size of the diamond. Also remember that carat weight is sometimes directly related to price. One three-carat diamond is always more expensive than several diamonds which add up to three carats.
weight is probably the easiest of the 4 C’s to understand. Diamond weight is measured in carats. There are 100 points in 1 carat (or 1 ct., when abbreviated). This means that a three quarter carat diamond can be referred to as “a 75-pointer” or “75 points”. Keep in mind that carat weight is only a measure of weight but not necessarily size (i.e. its measurements or the size it shows when facing up). The actual cut of a diamond will play a big role in the overall size of the diamond. Also remember that carat weight is sometimes directly related to price. One three-carat diamond is always more expensive than several diamonds which add up to three carats.
Although terms like “princess cut” and “cushion cut” are often used to describe diamonds, these are actually references to the diamond’s shape. , in the case of the 4 Cs of diamonds, refers to proper angling of a diamond’s to ideally reflect light and bring brilliance to the stone. Because light and sparkle are the most important parts of a diamond’s appearance, this is the most important of the 4 Cs of diamonds. According to the four Cs of diamonds chart, a good diamond that is badly cut is essentially ruined, while a less valuable diamond cut extremely well can become more attractive and valuable. Review our diamond color and clarity scale to choose the right diamond.Diamonds are graded on a scale from D-Z. Because of our high standards, deBebians sells only diamonds graded from D-J. On the diamond clarity scale, there are certain ranges within the GIA color grading scale. For example, a diamond graded D-F is considered to be colorless. Diamonds graded from G-H are considered to be near colorless.Generally speaking, the naked eye cannot tell the difference between one or two color grades on a loose diamond. Once a diamond is mounted into a setting the eye cannot tell the difference between three color grades. This means you can buy a F, G, or H color diamond and not really be able to detect much of a difference.The body color of a diamond is one of the 4 C’s that is detectable with the naked eye. A colorless diamond is colorless due to its ability to absorb rays of light equally. These diamonds are rare and expensive. Diamonds that are in the D-F range are considered colorless and carry a higher premium. Diamonds in the G-J range will face-up white and are sometimes a much better value than colorless diamonds. Diamonds that are K color or below will face-up with a slight hint of yellow.and its impact on diamond color: Fluorescence is a naturally occurring phenomenon in diamonds and it usually masks the overall body color of a diamond. Fluorescence is graded on a scale of none, faint, medium, strong and very strong. Generally fluorescence will mask the body color of a diamond to make the stone appear whiter. In other words, if you are seeking a diamond of a slightly lower color grade, looking for one with some fluorescence will make the diamond appear whiter.Most diamonds have inclusions. Therefore diamonds are graded on a scale from flawless (FL) to included (I3) to set them apart from one another. The less inclusions a diamond has, the rarer that particular diamond is, and the more valuable it is. deBebians sells only diamonds from IF to SI2. GIA and AGS have set standards for what classifies a diamond to have a particular grade. Please review our clarity chart for diamonds below that will better help explain each diamond grade’s typical characteristics.A good way to determine what clarity grade to select is to consider your budget. We recommend diamonds that are eye-clean — meaning you cannot see any of the inclusions by just looking at the diamond. This will include diamonds from IF usually down to the SI category. Please call us if you have any questions regarding a clarity grade. Our expert GIA Graduate Gemologists will be able to guide you in your search for that perfect diamond you are seeking.weight is probably the easiest of the 4 C’s to understand. Diamond weight is measured in carats. There are 100 points in 1 carat (or 1 ct., when abbreviated). This means that a three quarter carat diamond can be referred to as “a 75-pointer” or “75 points”. Keep in mind that carat weight is only a measure of weight but not necessarily size (i.e. its measurements or the size it shows when facing up). The actual cut of a diamond will play a big role in the overall size of the diamond. Also remember that carat weight is sometimes directly related to price. One three-carat diamond is always more expensive than several diamonds which add up to three carats.






