The Importance of Quality Auditing in Modern Business | monitorQA
Does your business understand the importance of quality auditing? Read on to learn about the different types of audits, common mistakes, and other actionable tips.
Audits can tell a person a lot about a business. They provide clarity on a company’s success and reassure investors, regulators, executives, and other stakeholders.
Quality auditing brings significant value to the organizations that use them. They’re a necessary component for optimizing growth, they evaluate how efficient a business is and help management identify if their current strategies deliver adequate results. In addition, quality audits identify the root causes of deficiencies so an organization can quickly take corrective actions.
Process, product, and system audits should be front and center of any quality management strategy. Read on to learn what quality auditing is, why it’s important, the advantages of quality audits, the principles behind them, the quality audit process, and why your quality audit may fail.
Mục lục
What is Quality Auditing?
Quality auditing refers to the independent, systematic, and well-documented examination of a company’s quality management system (QMS). Quality auditing aims to determine if an organization complies with the requirements within a specific quality system.
Because quality audits are a critical component of the ISO 9000 quality system standard, internal or external auditors or an auditing team usually perform them.
Why Auditing is Important
Audits are an integral part of regulatory and compliance requirements and are crucial for determining an organization’s existing or newly implemented success of products, systems, and processes.
Audits are vital for:
- Providing evidence for reducing and eliminating potential problem areas
- Discovering conformity or nonconformity of quality system elements with specific requirements
- Confirming objective evidence of processes
- Recognizing opportunities for improvement
- Deciding if products are suitable for use, safe for consumers, and compliant with regulations
- Determining whether an organization’s quality policies adequately meet quality standards
- Correcting deficiencies
For organizations to receive top benefit, quality auditing should showcase examples of good practice instead of just focusing on process issues, non-conformance, and corrective actions. This enables all departments to share information and adjust their working strategies accordingly to improve the organization continuously.

Advantages of Quality Audits
When an organization implements quality audits, there are numerous advantages:
- Encourage employees to reveal inadequacies when interpreting basic quality requirements
- Increase productivity by reducing mistakes and wasted materials, machinery, and human effort
- Internal quality audits improve both the quality of the system and the quality of the product
- Both internal and external quality audits evaluate the cost-effectiveness of quality systems and measure the effectiveness of quality programs
The Principles Behind a Quality Audit
Quality auditing is a powerful management tool used to assess reasons for poor quality, corrective actions that are needed, and confirm processes related to quality. Quality auditing detects problems or potential problems and defects in a company’s QMS and helps improve and resolve them based on findings and recommendations.
So, what can a quality audit do for your company?
- Provide assessment-based evidence
- Better collaboration
- Higher ethical standards
- Provide professional support
- Encourage independence
- Enhance confidence
- Improve proficiency
- Provide an accurate presentation
- Maintain objectivity
What is the Auditor’s Role?
An auditor is educated on the ins and outs of industry standards and conducts audits according to these standards. Quality auditors can be either internal or external:
- An internal auditor is an employee who understands company policies, procedures, and practices but isn’t directly involved in the product, system, or process audit
- An external auditor is an outside source hired from an approved agency, client, or customer with a complete understanding of the same policies, procedures, and practices of the industry

3 Types of Quality Audits
While there are many types of quality audits, they’re generally categorized as follows:
Classification #1: Process Audits
Process audits confirm whether a company’s processes are functioning within predetermined limits. They assess compliance to pre-established or industry standards and the strength of results from the existing process controls. Performing this type of audit highlights different parts of the procedures, such as:
- How they conform to processes concerning time, temperature, pressure, composition, and responsiveness
- The methods and materials used to perform the various controls and the environment that they take place in to determine the outcome
- The success and accuracy of the controls that are in place with proper training of procedures, instructions, and specifications
Classification #2: Product Audits
Product audits determine if a product or service complies with specifications, customer requirements, and performance standards.
Product and process audits are a big part of the manufacturing industry.
Classification #3: System Audit
System audits assess whether the components of an organization’s management system are appropriate, effective, developed, implemented, and documented according to specified requirements.
A QMS audit determines if the organization’s current quality management system conforms with company policies, regulatory requirements, and contract commitments.
Specific types of system audits include:
- Environmental system audits
- Safety system audits
- Food safety system audits
What’s the Difference Between First-, Second-, & Third-Party Audits?
First-Party Audits
First-party audits are internal audits completed by employees who don’t have a direct correlation to the audit results. First-party audits:
- Measure a company’s performance according to its objectives
- Identify problem areas
- Find ways to improve strategies, processes, and performance continuously
Second-Party Audits
Second-party audits are external audits completed by auditors hired from outside the audited organization. Second-party audits are more formal than first-party audits due to the audit results potentially impacting customers’ purchasing decisions.
Third-Party Audits
Third-party audits are external audits completed by independent organizations to eliminate conflict of interest. Third-party audits can result in license approval, recognition, certification, fines, or penalties issued by the external auditing organization.
Handling the Quality Audit Process
Handling the quality audit process can be challenging without proper direction:
Step #1: Determine the Scope of Your Audit
Before deciding on an auditor, you need to determine the scope of your internal audit. Assign this task to your quality-control manager or someone in a similar role. The criteria of your audit should focus on high-risk areas of the organization and process lifestyle and should stay consistent wherever possible. Your goal is to analyze performance and give your employees clear direction between audits.
Step #2: Plan & Prepare for Your Audit
To ensure a successful audit, spend some time preparing it. An organization’s first priority is to designate an internal or external auditor. Then, work with your auditor to determine the format of your audit, and allow sufficient time before starting the audit. Thorough planning and preparation of the audit process should include:
- Scheduling timed intervals with advance notice of when the audits will take place
- Determining the number of resources needed to complete the audit
- Gathering and organizing the required paperwork
- Completing the audit
- Reporting the results
- Determining the accuracy of procedures
- Following up on corrective actions
Step #3: Carrying Out the Audit
The “fieldwork” stage of the auditing process includes:
- Interviewing employees
- On-site audit management
- Evaluating process and system controls
- Ongoing communication with relevant employees throughout the organization
- An exit meeting between the auditee and auditor
Step #4: Reporting and Follow-Up
An audit report details the results of an audit investigation and provides organizations with accurate data on conformance, non-conformance, management, and recommendations on corrective actions. A thorough audit report allows organizations to effectively track quality, performance, and areas needing improvement and showcases company successes and achievements.
Step #5: Corrective Actions
When an audit determines areas of non-compliance with company or industry standards, the organization needs to act on the problems immediately. Start by focusing on one or two main areas requiring corrective actions and regularly monitor the progress. Continuous improvement involving all employees is key to ensuring compliance with quality standards over time.
![]()
5 Reasons Why Your Quality Audit May Fail
Some companies adopt the ISO 9000 standards to ensure compliance with regulatory requirements and prove their commitment to quality assurance to their stakeholders.
Tech Target.com defines ISO 9000 as a series of standards developed and published by the ISO (International Organization for Standardization), put in place to define, establish, and maintain an effective quality assurance system for service and manufacturing industries.
Not all companies have a quality assurance system, and some that do may not implement it properly, leading to an audit failure.
Here are five reasons why your audit may fail:
Reason #1: Poor Documentation
Your quality audits can easily fail without proper documentation. Therefore, it’s important to properly organize, store, and manage your data in one central hub to avoid failure due to poor documentation.
Reason #2: Improper Enforcement Strategies
Knowledge is power. Ensure your staff is well-trained with a clear understanding of the enforcement strategies within your industry. Collaborate with a good strategy that appropriately addresses any non-conformance issues within your organization.
Reason #3: Not Understanding How ISO Works
Not understanding ISO compliance and standardization is a common mistake among business owners—many believe that ISO awards companies with certification, but it’s actually the independent certification bodies that certify companies. Proper ISO understanding is a must for passing your audit with flying colors.
Reason #4: Choosing Your Auditor Too Quickly
Deciding on the best auditor to use for your business shouldn’t be taken lightly. Poor auditor selection can drastically affect your compliance. When auditors are chosen too quickly without consideration or adequate research, it could negatively impact your entire auditing process.
Reason #5: Lack of Competency Testing
Another aspect of ISO 9000 quality management is employee competency testing. Many companies ignore or intentionally leave competency testing out of their quality management strategies and later pay for it during the auditing process. Proper training focusing on awareness of quality goals should be done every year.
Looking For the Best Auditing Software For Your Business?
Simplify your quality auditing inspection process with monitorQA’s flexible, intuitive, and fully customizable mobile inspection software designed for busy people on the go.
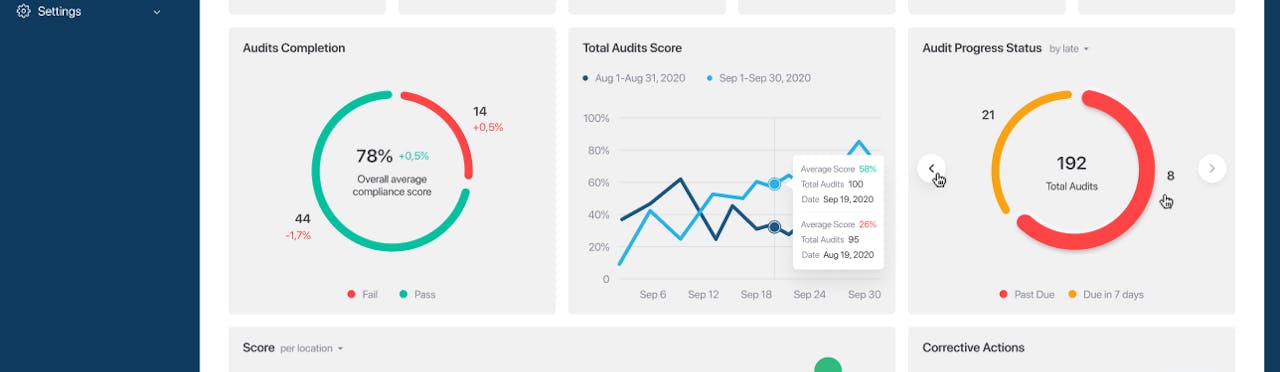
monitorQA makes compliance easy by putting quality auditing at the top of your to-do list:
- Streamline compliance audits
- Improve your health, safety, and quality standards
- Get complete visibility into your daily operations
- Stay on top of corrective actions
- Use the smart audit form builder to quickly customize, auto-fill, and skip steps using conditional logic
- Eliminate paper forms for good—no more wasted time or manual reporting
See what else monitorQA can do for your business today.
Try for Free






