Ultimate Diamond Buying Guide 2023
Pro tip: If you’re in a hurry, take this PriceScope Diamond Buying Shortcut.
Mục lục
1. How To Choose The Right Diamond Shape?
*PriceScope Priceless Tip: Shapes other than round are not graded for cut, which is the most important C.
Diamond Shape is the starting point for any diamond buying decision. When gifting a diamond, it’s extremely important to knowing the wearer’s preferred shape and choice of style.
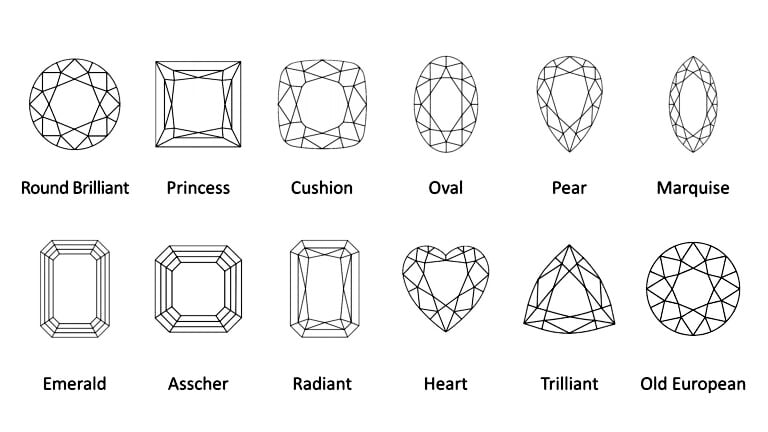
What Diamond Shapes Are There?
The vast majority of diamonds are round but other options exist, some of which are quite unique.
Diamond Shapes Chart
What Is Diamond Length To Width Ratio?
This ratio numerically illustrates how long and wide the stone appears from the face-up view. Expressed as “L:W”, it’s determined by dividing the length of the diamond by its width. For example, if a diamond had a length of 6.00 mm and a width of 4.00 mm, the length-to-width ratio would be 1:5.
Which Length To Width Ratio Is Best For Each Shape?
Suggested Length-to-Width Ratio Chart
-
Round Brilliant: 1.0 – 1.03
-
Princess: 1.0 – 1.05
-
Cushion (square): 1.0 – 1.09
-
Cushion (rectangular): 1.15 – 1.25
-
Emerald: 1.50 – 1.75
-
Asscher: 1.0 – 1.05
-
Oval: 1.30 – 1.50
-
Pear: 1.45 – 1.75
-
Marquise: 1.85 – 2.1
-
Radiant (square): 1.0 – 1.05
-
Radiant (rectangular): 1.15 – 2.0
-
Heart: 1.0 – 1.1
-
Trillion: 1.0 – 1.1
-
Baguette: Around 5.1
Which Diamond Shape Looks The Biggest?
This is sometimes referred to as the ‘face-up’ size. Diamonds with a bigger face-up value will have a larger surface area relative to their carat weight. In general, compared to the round brilliant, these diamond shapes may offer a larger size-for-weight appearance.
-
Pear
-
Oval
-
Marquise
-
Emerald
-
Trillion
Which Diamond Shapes Are The Most Affordable?
The most affordable diamond shapes are those which retain a higher percentage of the rough during the cutting and polishing process. In general, compared to the round-brilliant, these diamond shapes may offer more weight for the money, although they may not look as large for their weight.
-
Radiant
-
Cushion
-
Princess
-
Asscher
-
Emerald
Which Diamond Shape Gives The Best Sparkle?
Sparkle is created by facets reflecting light effectively. A good quality cut will increase sparkle, but by nature, some diamond shapes sparkle more than others.
-
Round Brilliant
-
Radiant
-
Cushion
-
Marquise
Which Diamond Shape Is The Most Vulnerable?
Certain diamond shapes have vulnerabilities which can affect durability if they are not set correctly. Any of these diamond shapes with exposed points and corners are more vulnerable to chipping. This is easily handled by choosing a suitable setting.
-
Pear
-
Marquise
-
Baguette
-
Princess
-
Heart
What Diamond Shape Holds Its Value?
The round brilliant diamond holds its value best of all shapes. Additionally, collection quality round brilliants has historically held and increased in value best over time, especially auctionable diamonds of a significant carat weight and value. Collection quality diamonds have a special status in the eyes of many diamond professionals, collectors, enthusiasts, and auction houses.
2. How To Choose The Right Diamond Carat Weight For Your Budget?
*PriceScope Priceless Tip: You can’t judge a diamond’s size by its carat weight, you need more information.
Diamond carat weight has the most impact on value but you can’t judge a diamond’s visual size by its weight, nor even its physical dimensions. Bright jewelry store lights make all diamonds look bright and big. When removed from spotlights, many diamonds go dark at the edges, seeming to shrink before your eyes. Read on and learn how to avoid this.
What Is Diamond Carat?
One diamond carat equals 200 milligrams. Putting that in perspective, a small paperclip weighs about 600 milligrams, so a paper clip on your finger weighs about the same as a three-carat diamond. A carat can also be divided into 100 points, so jewelers call a 1/4 carat diamond a 25-point diamond, a 1/2 carat diamond a 50-pointer, and so on.
Does Carat Size Matter?
Yes, but you will also want to know the diamond’s physical spread from side to side, to ensure it “faces-up” the correct size for its weight.
What Is Total Carat Weight?
The term “total carat weight” (abbreviated ctw) refers to the sum of all diamonds in a piece of jewelry. A halo ring with a 0.75-carat center stone and 0.25 carats in small surrounding stones can be advertised as having 1.00-carat total weight or “1ctw.” Likewise, a bracelet with twenty 0.10 carat diamonds may be advertised as a 2.00 carats total weight bracelet, or “2ctw.”
How To Choose Carat Weight With Confidence?
Diamond Cut Quality works in tandem with carat weight. The way a diamond is cut determined whether it has proper physical spread and proper visual spread. Choosing a diamond with superior cut quality is the best way to be confident you’re getting the best visual appeal and size appearance for the carat weight.
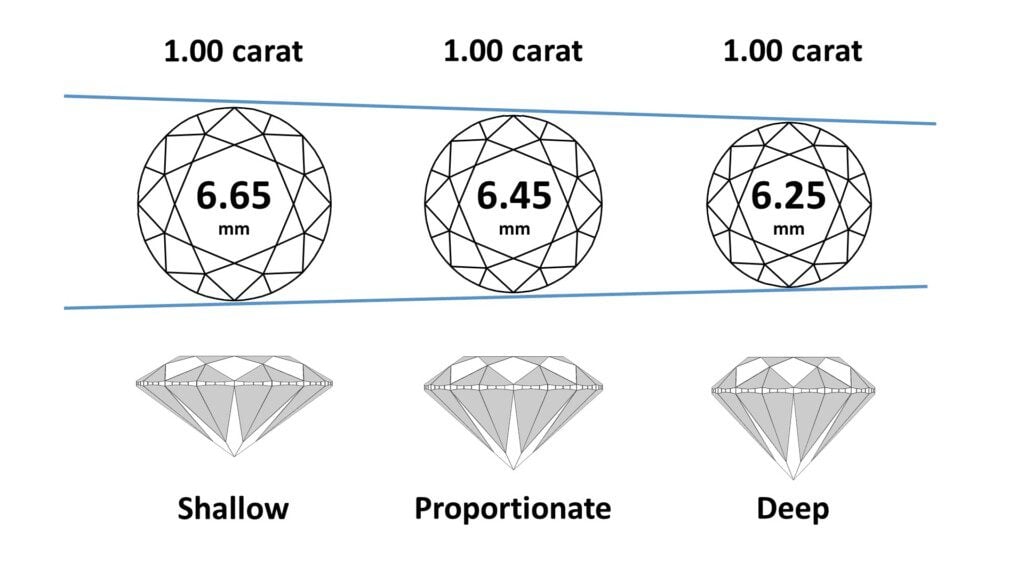
How Does Proportionate Spread Affect Carat Weight?
Diamonds cut shallow or deep go dark in some lighting or environmental conditions, looking smaller than they should for their carat weight. Be sure to correlate carat weight with side-to-side spread in millimeters. A diamond’s grading report will include its external measurements in millimeters, from which you can determine its physical spread, side to side.
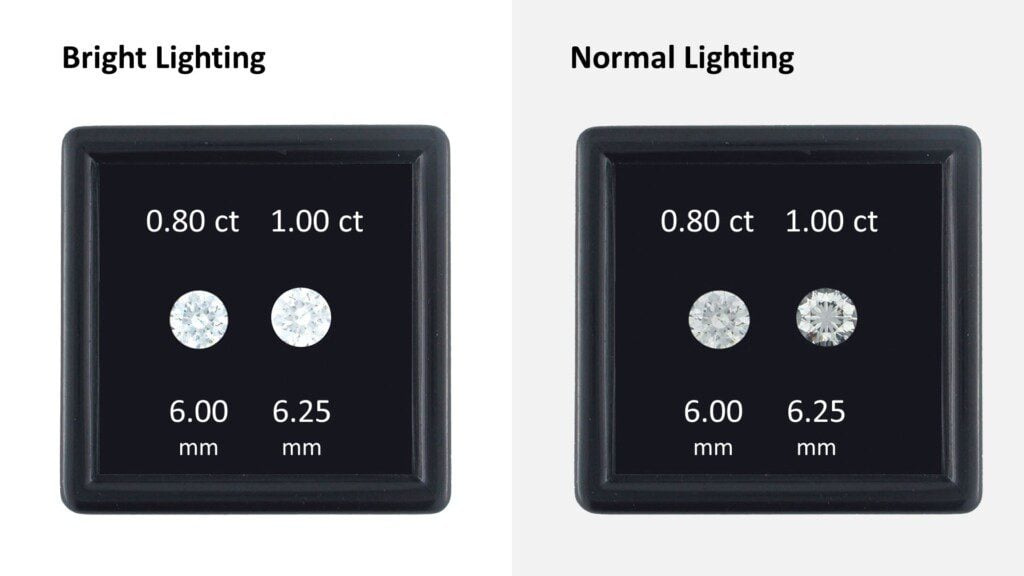
What Is A Good Carat Weight?
The best carat weight is one that has proper physical and visual spread, looking as large as it should in all lighting environments. Choosing a 1.00 ct diamond over an 0.80 ct diamond makes no sense if the 0.80 ct diamond appears larger than the 1.00 ct diamond in normal lighting.

3. Why Does Diamond Cut Matter?
*PriceScope Priceless Tip: Unlike color and clarity, where high grades are strict and rare, more than 60% of round brilliants receive the “Excellent” cut grade, so you need more information to make decisions.
Cut is the most important diamond C: In strict diamond grading systems the highest color and clarity ratings show little or no visible differences across several grades. Alternately, several diamonds with the same “top” cut rating can vary notably in appearance. More than 60% of round diamonds receive the “Excellent” cut grade but some look far better than others. The way a diamond is cut drives all of its various Diamond Performance components.
How Is Diamond Cut Graded?
Diamond Cut grading is treated differently from lab to lab. Why? Because color and clarity have been strictly graded since the 1950s, but the world’s largest laboratory, the Gemological Institute of America (GIA), didn’t grade cut until 2006. By then, other diamonds ratings systems for cut had been launched by other laboratories. As a result, there are a number of different approaches to grading cut. Cut grading is also different than color and clarity grading because, in strict diamond grading systems the highest color and clarity ratings show little or no visible differences across several grades. Alternately, several diamonds with the same “top” cut grade can vary notably in appearance.
Why Is Diamond Cut Important?
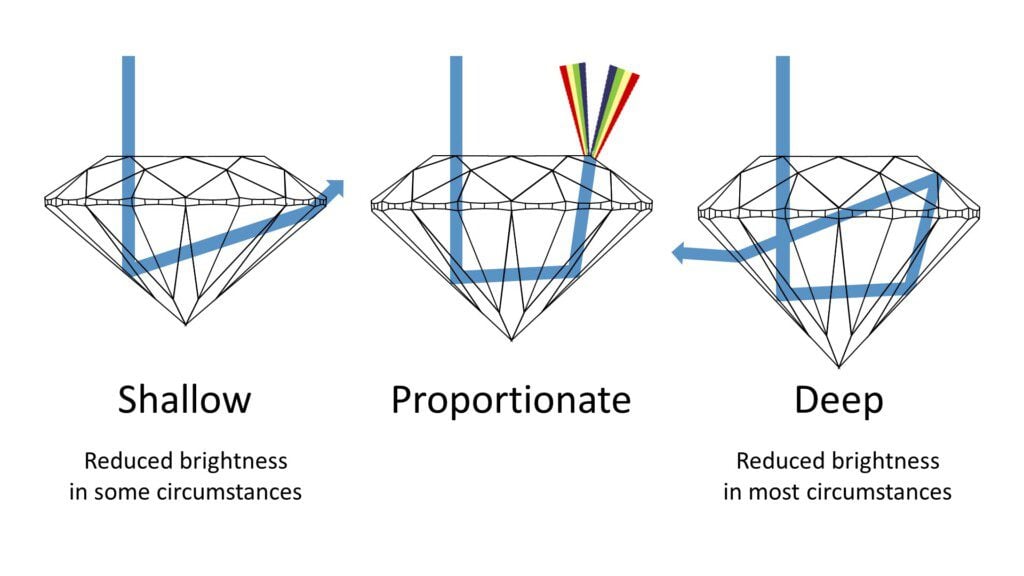
Superior diamond cut quality can improve every other diamond C in appearance. Well cut diamonds have proper physical spread, as well as edge to edge brightness for maximum visual spread, so they appear large for their carat-weight. In well cut diamonds light gets in and out on shorter ray-paths with greater intensity, improving face-up diamond color appearance. Well cut diamonds promote more visible brightness, dispersion, contrast and – in brilliant shapes – scintillation, which can mask inclusions. And well cut diamonds have brighter, more dynamic diamond performance qualities – widely considered their most appealing aspect.
Are Diamonds Cut For Weight Over Beauty?
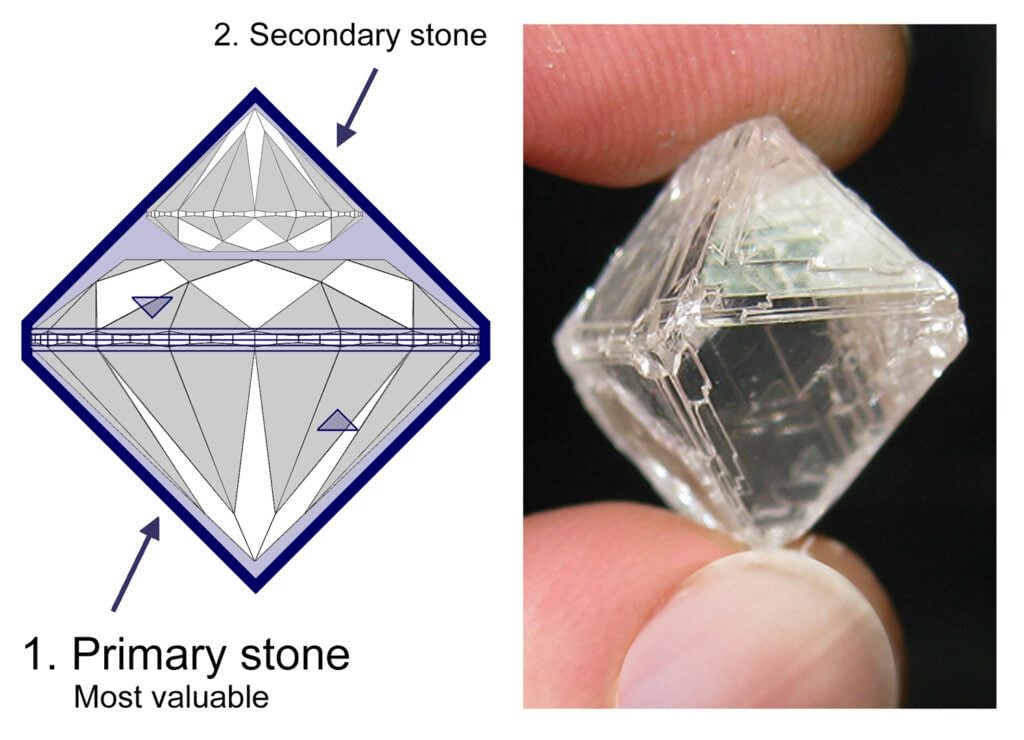
Yes. Unfortunately most diamonds are not cut well because carat weight has the most influence on price. That motivates diamond producers, when planning, to keep the most possible weight in the diamond. The typical rough diamond octahedron produces two finished diamonds. The primary stone has the most value. Diamond producers profit most by using angles as close to the rough outline as possible (circa 45 degrees) which can still earn a favorable grade like “Excellent” or “Ideal.” However, those angles often aren’t the best for brightness, resulting in darker, less lively diamonds.

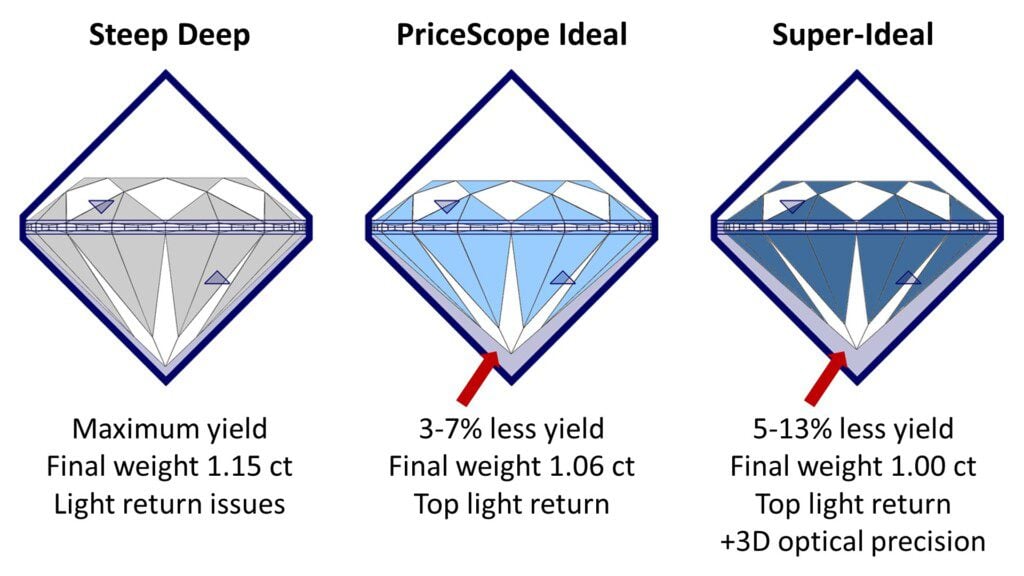
What Are The Diamond Cut Subsets?
The PriceScope community refers to several subsets of round brilliant diamonds. Steep-deep diamonds are most abundant. Producers use wide (steep deep) cutting angles to increase the diamond’s final weight, maximizing yield. Unfortunately this reduces their size appearance and creates darkness when removed from bright lights. The PriceScope Ideal is cut with proportionate angles which successfully reflect and return light back to the viewer’s eyes as brightness, fire, contrast, and sparkle. The Super-Ideal is a rare subset, cut within a small range of scientifically proven “ideal” proportions and further fine-tuned to display Hearts & Arrows in a specialized viewer.
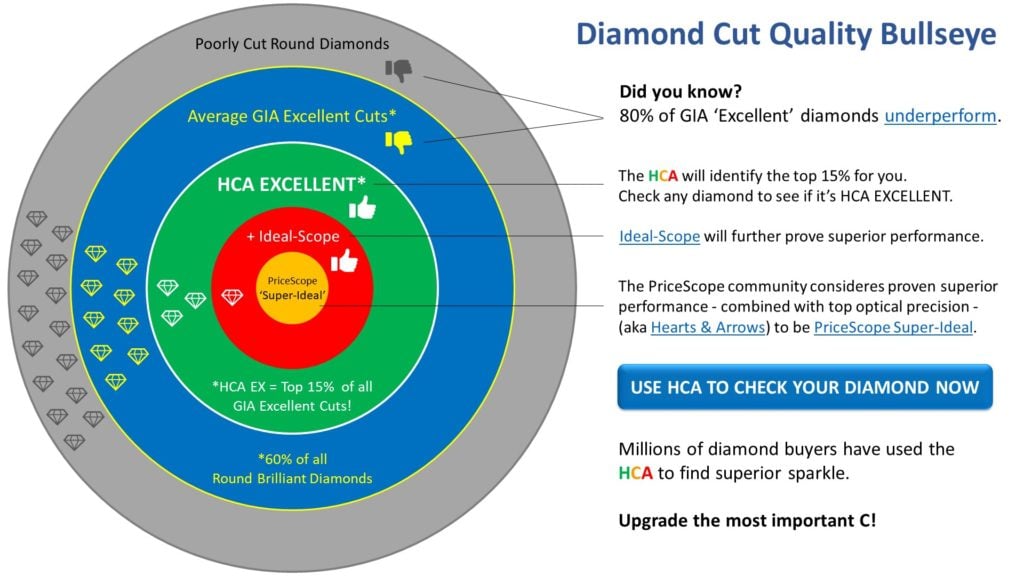
What Is The Holloway Cut Advisor?
The Holloway Cut Advisor (HCA) is an analytic tool that uses measurements of a round brilliant diamond to calculate potential light return, fire, scintillation and spread. When you register with PriceScope you can analyze three diamonds for free. HCA scores are also included in PriceScope round diamond search results.
Use Our HCA To Hit The Cut Quality Bullseye
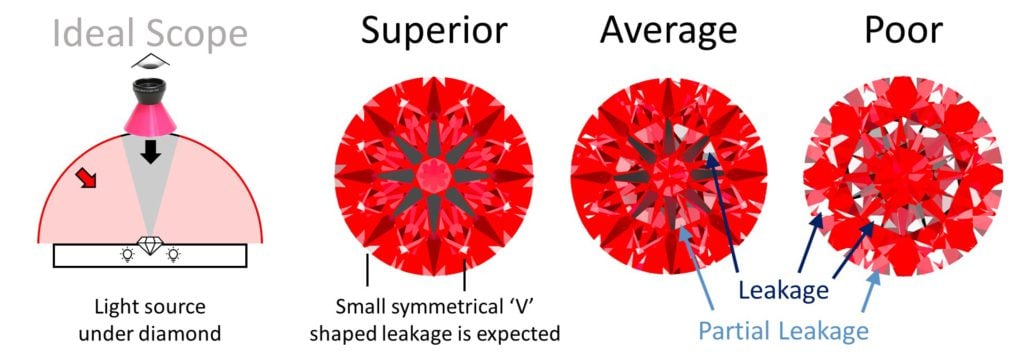
What is Ideal Scope?
The Ideal Scope is a portable diamond brilliance and leakage gauge. A lens with a hot pink reflector lets you see how much light comes from a diamond to your eyes. The most brilliant diamonds have pink/red (brightness) with a symmetrical black star (contrast) and minimal white or pale areas (leakage).
What Are The Key Steps To Assessing Diamond Cut?
For round brilliant diamonds, start by getting the average proportions. Enter those, or the grading report number, into the patented Holloway Cut Advisor (HCA) tool on PriceScope. For diamonds considered HCA Excellent, ask the seller for a Performance Scope Image – either Ideal Scope or ASET. If the seller doesn’t have such an image, they can use a 3D scan of the diamond to produce one using computer modeling. In-person viewing. Ultimately you want to select only the best cut diamond or diamonds and make comparisons with an In-Person Viewing exercise.
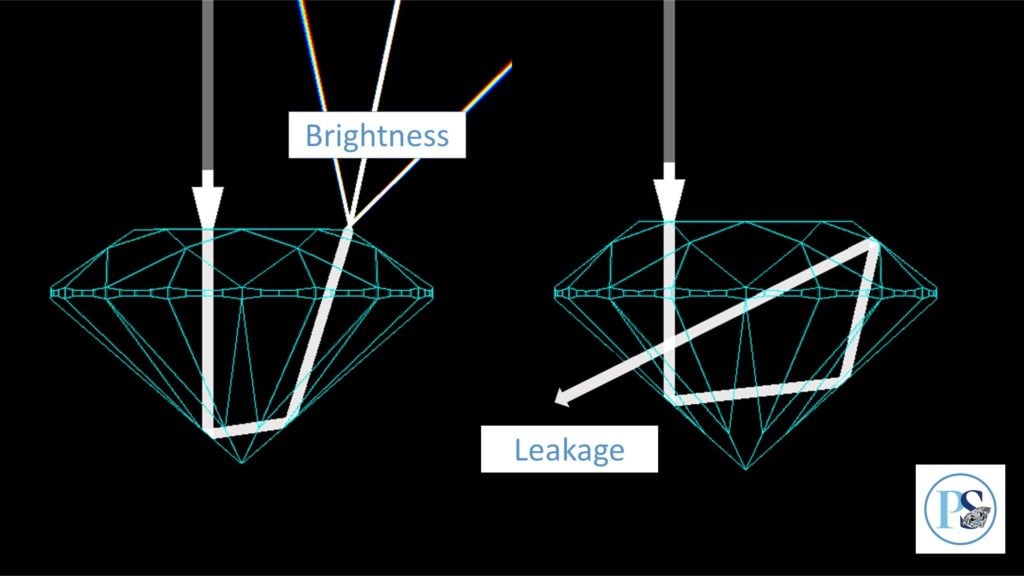
What Is Diamond Leakage?
Light entering a diamond will either reflect and shoot up to the viewer’s eyes (as brightness) or escape through the bottom (as leakage or windowing). In general terms, brightness is desirable, leakage is to be avoided.
4. How To Choose The Right Diamond Color?
*PriceScope Priceless Tip: The most purchased diamond colors are F-G-H or I, set in white gold or platinum.
Diamond Color influences price the most after carat weight. A diamond’s color was caused by chemicals in the earth where it formed. Most of the world’s diamonds are yellow or brown. The objective for most people is to get a diamond that appears colorless, also described as “white.”
How Is Diamond Color Graded?
Most diamonds are graded on a scale ranging from D, which has the least color, all the way to Z, which is light yellow or possibly light brown. Other colors, and stronger levels of yellow and brown, are classified as fancy colored diamonds, and are graded on a different scale.
Do I Need To Spend Big To Get A Colorless Stone?
Most people cannot detect a difference of 2-3 color grades unless the diamonds are placed next to each other, especially in the colorless (D-E-F) and near-colorless (G-H-I-J) ranges. With that said, taste comes into play. For those who love the icy appearance and rarity of a colorless diamond the extra spend may be worth it.
How Does Diamond Shape Affect Color?
Fancy shapes may reveal more color than round brilliant cuts in the face up position because they have broader facet arrangements. This is largely a non-factor in diamonds graded DEF. The potential for more visible color appearance or color concentration increases the more you consider diamonds graded GHIJ and below.
Is diamond color graded upside down?
Yes. Gemological laboratories perform D to Z color grading with the diamond upside down and viewed through the side because of three factors which may influence color appearance in the “face-up” position: The diamond’s shape, the way the diamond was cut and the possible presence of diamond fluorescence.
Do Larger Diamonds Show More Color?
Yes. As they get larger in size, diamonds show more color. As diamonds increase in carat weight the presence of color becomes more noticeable, simply because whatever color exists throughout the diamond occurs takes on more mass. The presence of color in diamonds graded K and below becomes especially noticeable at weights above 2.50 – 3.00 carats.
What Is Undisclosed Undertone?
Undisclosed undertone is something that isn’t disclosed on diamond grading reports. It’s a subtle or not-so-subtle brown, grey or green undertone which influences overall color appearance. This issue is disclosed among traders but isn’t always communicated by diamond sellers to consumers.
How Does Cut Affect Diamond Color?
Remember that diamonds are color-graded upside down, viewed through the side. “Face-up” color is the diamond’s color appearance when viewed from the top. In well-cut diamonds light gets in and out on shorter ray-paths with greater intensity. This can cause the appearance of less color when the diamond is seen from the top.
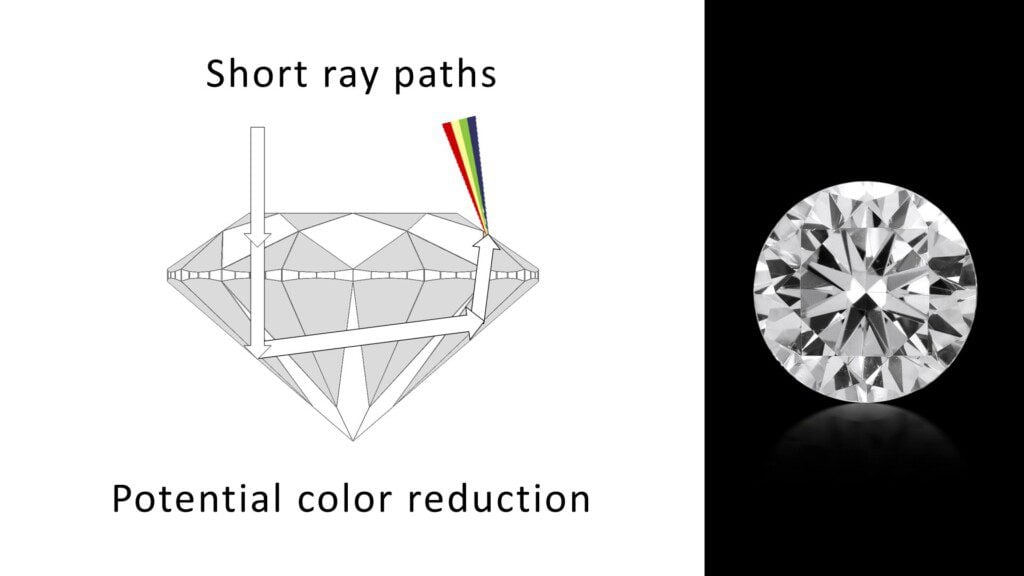
Alternately, if the diamond is cut so that light escapes through the bottom – or bounces around inside – the color within that diamond may be exaggerated when seen from the top.
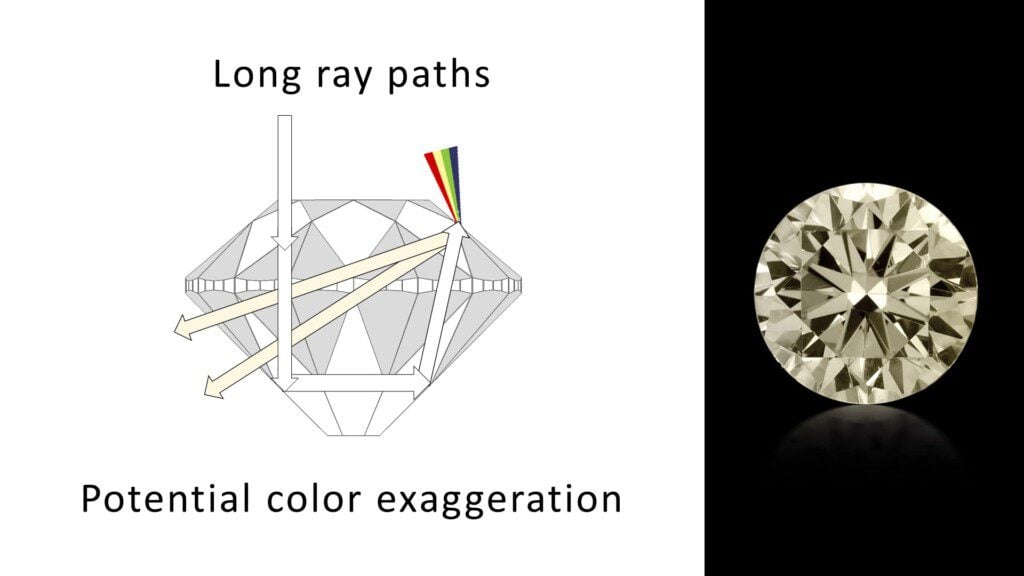
Which Diamond Colors Are Recommended For Different Ring Settings?
Round brilliant diamonds benefit from kite-shaped facets which promote sparkle, so they can be set in white metal in colors from D-J. Colors below J are well-suited for yellow metal settings. Colors with brown undertone look great in rose-gold settings. Fancy shapes are recommended for setting on a different schedule. See all metal recommendations here.
Does Color Affect Diamond Price?
Diamond Color influences price the most after carat weight. Collection quality diamonds are those with color and clarity combinations which trade for the highest values and continue to hold that value best over time. Combining a non fluorescent, D color, E color, or F color with Flawless, Internally-Flawless, VVS1 or VVS2 clarity gives a diamond collection quality status in the eyes of diamond professionals and enthusiasts. Some people choose high color and clarity combinations for this reason.
5. How Do You Choose The Right Diamond Clarity?
*PriceScope Priceless Tip: The most purchased clarity grades are VS1, VS2 and “eye clean” SI1.
– Definition on diamond clarity.
What Is Diamond Clarity?
The world’s natural diamonds formed between 1-3 billion years ago, 100 miles beneath the earth’s surface. As they grew, chemicals and elements present in the earth became trapped within their crystal lattices. Diamond Clarity evaluates a gemstone’s relative freedom from such internal characteristics, classified as inclusions, and from surface characteristics, classified as blemishes.
How Is Diamond Clarity Graded?
A gemologist analyzes clarity by looking down through the top of the stone at 10-power (10X) magnification. All inclusions and blemishes seen at 10X are considered when deciding the clarity grade. There are 11 different clarity grades.
What Are Inclusions?
Inclusions are characteristics trapped within the diamond.
What Is An Eye-Clean Diamond?
Many people just want an “eye-clean” diamond, meaning one which has no inclusions invisible to the naked eye. There is no laboratory definition for this, but a PriceScope survey of gemologists resulted in this consensus:
Eye-Clean: No inclusions visible to the unaided eye when viewed from the face up position in daylight equivalent or fluorescent lighting between 6-12 inches from the eye using 20/20 vision.*
See a diamond clarity chart showing eye-clean clarity grades.
Eye Clean VS 10x, What’s The Difference?
Eye-clean is determined when viewing a diamond with the naked human eye. 10X examination is performed viewing the diamond with a magnifying loupe or microscope.
How To Assess Diamond Clarity Confidently?
Successful online sellers like our recommended PriceScope vetted vendors, have methods of reliably classifying and communicating diamond clarity, whether you’re examining it in-person or purchasing online. They also offer liberal inspection periods and free returns so you can make your purchase with complete confidence. You can read about how to choose diamond clarity with confidence here.
What Factors Affect Diamond Clarity?
In addition to visibility at 10 power magnification, gemologists also consider Location, Number, Color, Size and the Nature of inclusions and blemishes when deciding the diamond clarity grade. You can read definitions for each of those additional factors on our Diamond Clarity page.
What Are Clouds Not Shown?
In clarity categories VS2, SI1, SI2 and below the comments “clouds not shown” or “additional clouds not shown” typically indicate the diamond grader considered them a non-issue. The comment is simply on the record for other gemologists who may examine the diamond later.
What Is Diamond Clarity Haze?
Since clarity grading is limited to 10X magnification characteristics beyond that scrutiny can go unreported. Undisclosed diamond haze is caused by large clouds of microscopic pinpoints when they become dense enough to interfere with light transmission and reduce transparency.
What Are Sleepy Stones?
Trade members may refer to hazy diamonds as being “sleepy stones,” a phenomenon which occurs on a sliding scale. Slight cases may not even be noticed by the average jeweler. In moderate cases the diamond will seem to need a cleaning when seen in some lighting environments. In the most severe cases the diamond is notably reduced in its performance qualities in all lighting environments.
6. How To Choose The Right Diamond Vendor?
*PriceScope Priceless Tip: For risk-free purchases, generous policies and robust consumer protection, consult our list of 5-star PriceScope Vetted Vendors.
As the world’s largest diamond and jewelry community, PriceScope is a place where many would like to advertise and list products. Few meet our standards. PriceScope Vetted Vendors provide safe online purchase experiences with generous inspection periods, hassle-free returns, and standout long-term benefits for clients.
Who Are Trusted PriceScope Diamond Vendors?
PriceScope’s Vetted Vendors meet or exceed PriceScope’s rigorous requirements for truthful advertising, best business practices, and proactive consumer protection. They deliver the high-quality customer service standards developed by over 100,000 PriceScope members over the past 20 years.
How Do We Assess Our Recommended Vendors?
We take the trust of our members very seriously – to protect our diamond and jewelry community, each of our potential associations involve a thorough vetting process. This often takes more time and effort, but it helps ensure the vendors who meet our requirements are the most consumer-friendly, setting industry benchmarks in truthful advertising, best business practices and consumer protection.
What Principles Do We Stand By For Our Vendors?
Components we have considered include, but are not limited to: Company history, including founders/owners, reviews/ratings and references. Truthful advertising, including messaging philosophies, proper promotion of strengths, proper use of terminology and industry esprit de corps. And best business practices and consumer protection through product selection, information provision, education, policies and short, mid and long-term client experience.
7. Do I Need A Diamond Certification?
*PriceScope Priceless Tip: Make sure your diamond comes with a grading report from the GIA, IGI, AGS or GCAL.
What Is A Diamond Certification?
Diamond Certificates (or grading reports) are issued by an independent gemological laboratory, following a secure, standardized diamond grading process. It’s an assessment of the diamond’s 4Cs, which are used to establish its value.
Who Is The GIA?
The GIA is the most widely recognized gemological institute, considered the world’s foremost authority on diamonds, colored stones, and pearls. A public benefit, nonprofit institute, the GIA has been the leading source of knowledge, standards, and education in gems and jewelry.
Who Is The IGI?
The IGI is the world’s largest gemological organization, operating 18 laboratories and 14 schools of gemology around the world. In addition to being the world leader in lab-grown diamond grading IGI issues grading reports for finished jewelry, serving more consumers than any other lab.
Who Is The AGS?
The AGS began grading diamonds in 1996 and is best known for their strict cut and performance standards. The AGS Platinum Report is the certificate of choice for diamond brands renowned for superior cut quality. They are one of two top-tier laboratories offering cut quality assessments for certain fancy shapes.
Who Is The GCAL?
The GCAL, established in 2001, is the only laboratory issuing diamond “certificates” backed by a guarantee. The GCAL focuses on diamond cut analysis, using a copyrighted diamond-specific performance assessment method, and provides a unique diamond fingerprint known as Gemprint. They are one of two top-tier laboratories offering cut quality assessments for certain fancy shapes.
How Do Standards Vary Across Certifications?
Generic reports accompanying economical pieces like those seen in mall or department store jewelry counters should not be confused with loose diamond certification (or grading reports). These documents are not item-specific, they are mass-produced to describe a production run of numerous similar pieces. They are not nearly as strict, accurate or expensive as stand-alone diamond grading reports or jewelry identification reports, prepared for a specific piece.
Is Carat Weight Universal?
Yes. Diamond grading scales are calibrated to three decimal places. Most laboratories establish carat weight to two decimal places, with the exception of the AGS, which reports to three.
How Are Color and Clarity Grades Certified?
Diamond color employs the alphabet, starting with D (colorless) and progressing from E to Z as the presence of tint increases. Diamond clarity uses a set of acronyms in a diamond ratings system which is not as intuitive as color and clarity. The grades are subjective decisions made by trained gemologists examining the stones.
How Are Cut Grades Certified?
Diamond cut grading is treated differently from lab to lab. Why? Because color and clarity have been strictly graded since the 1950s, but the world’s largest laboratory, the Gemological Institute of America (GIA), didn’t grade cut until 2006. By then, other diamonds ratings systems for cut had been launched by other laboratories. As a result, there are a number of different approaches to grading cut.
What Is Diamond Standard Deviation?
No two diamonds are alike. Color and clarity occur on a sliding scale and a diamond sitting directly on the border of two grades may come out on one side of the other, depending on the subjective opinion of the gemologist making the judgment. To that end, a standard deviation of +/- one grade is generally deemed acceptable among professionals.
What Is An Under Graded Diamond?
Under grading occurs when a jewelry professional intentionally claims a diamond has lower grades than it would normally receive according to strict, industry-accepted international standards. The goal of intentional under-grading is to win consumer business by creating fear-based doubts about other professionals.
Is It Worth Buying A Certified Diamond?
Any diamond of value should be accompanied by a grading report from a top-tier laboratory. Expensive jewelry pieces should either be accompanied by a finished jewelry grading report or, at minimum, come with a grading report describing the central gemstone. For inexpensive pieces, full grading may not be practical.
How Much Does A Diamond Certification Cost?
Laboratory analysis and grading charges are largely based on the diamond’s carat weight. For a one-carat loose diamond, the charge has historically landed near $100. There are many services offered by the different grading laboratories. Consumers may contact them for full explanation of services and fees.
Are Diamonds Certified The same?
Presuming you stay with certification from a top-tier diamond certification laboratory, diamond ratings for color and clarity will typically remain within one grade for any specific diamond. Considering how granular and subtle those diamond ratings systems are, a one grade difference is technically negligible. Of course, those values are used to establish a diamond’s value so it’s in the best interest of shoppers to use the strictest set of grades.
8. How To Take Care Of Your Diamond?
*PriceScope Priceless Tip: Do not expose gemstone jewelry to mechanical cleaners. Learn our Seven Steps to Sparkle.
Your jewelry was designed to be worn. Frequently and proudly. You will be able to keep your jewelry in top condition by learning How to Clean Jewelry.
Should I Clean My Diamond Regularly?
Yes. Each day, before retiring follow this Careful Cleaning Credo: Remove all jewelry and wipe each piece down with a clean soft dry cloth to remove perspiration, chemicals, etc. This prevents buildup and helps maintain optimum beauty between professional cleanings.
Should I Insure My Diamond?
Engagement Ring Insurance is a personal decision, but diamond is the hardest material known to man, but even the most flawless diamond can chip if struck along its crystal’s cleavage plane. For this reason, we believe every diamond owner should carry insurance.
Should I Get My Diamond Inspected Regularly?
Yes. Enlist the help of a professional jeweler every so often to deep-clean and check integrity. How frequently depends on your wear habits – as a general rule we recommend once or twice per year.
How To Bring Back The Diamonds Sparkle?
Periodically it’s prudent to perform thorough home jewelry cleaning. Due to their superior hardness, toughness, and stability, there is a seven-step process that can be safely performed with diamonds. Other jewelry should be considered on a case-by-case basis.
How To Prevent My Diamond From Getting Cloudy?
Clean the bottom of the diamond regularly with a soft brush. Light enters the stone from above, but the bottom facets play a critical role in both reflection, which helps the stone be bright, as well as refraction. Light that would normally reflect gets drawn out by grease or oil on the underside. This mutes how diamonds and gemstones sparkle.
Should I Use A Professional To Clean My Diamond?
If you clean your diamond and gemstone jewelry after each use according to this credo, and additionally clean daily-wear jewelry using these careful seven steps once per week your visits to a professional will be less frequent. Nevertheless, for deep cleaning we recommend visiting your jewelry pro once or twice per year.






