Verification and Validation in Testing: When to use which?
Table of Contents
Before diving into the difference between verification and validation testing, let’s take a moment to answer the question: “What is Verification and Validation in software testing?”
Mục lục
What is Verification Testing?
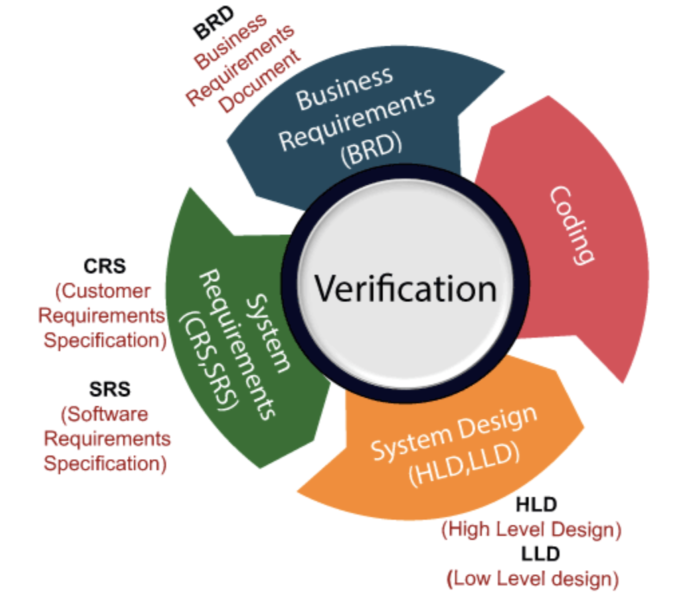
The IEEE-STD-610, a set of software engineering standards, defined verification testing as “A test of a system to prove that it meets all its specified requirements at a particular stage of its development.”
In other words, verification testing is the process of examining all predetermined software specifications – documents, code, design, and program – to ensure that the software is meeting these specifications. Some important documents to be reviewed in this stage are requirements specification, design blueprints, ER diagrams, database table design, test cases and scenarios, traceability matrix, etc.
Verification tests ensure that all development elements (software, hardware, documentation, and human resources) adhere to organizational and team-specific standards and protocols. It checks to authenticate that the system design and architecture are accurately engineered and free of errors.
In the official definition, notice the phrase “at a particular stage of its development”. A single verification test applies to a single stage in the development process. Before development begins, a set of standards and requirements are established for each stage in the process. Verification testing checks software that is in the middle of being developed to ensure that it complies with these standards.
Often, verification checks are something like studying the specifications and checking them against the code logic. Code reviews, walkthroughs, inspections, design, and specification analysis are common components of verification testing.
Advantages of Verification Testing
- Early and frequent verification reduces the number of bugs and defects that may show up in later stages.
- By verifying at each stage, devs, product managers, and stakeholders can get more insight into what the product may need to be developed better in the coming stages.
- Even if they can’t solve all bugs immediately, verifying helps QAs estimate the kind of issues that might emerge and help them better prepare to handle those when they appear.
- Verification helps keep software closely aligned with customers and business requirements at every stage. This ensures that devs have to put in less unnecessary work as development continues.
Read More: How to create test scenarios with examples
When to use Verification Testing
Verification tests must be run at every stage of development before any feature is implemented.
For example, let’s consider a button labeled “Add to Cart”. Before starting off with creating this button, verification tests would look through all relevant requirements previously decided in the ideation and brainstorming phases.
Let’s say the documentation says the button must be black with the lettering in white. It should be no larger than 10mm X 10mm, and it should be constantly visible in the top right corner of every product page of the website. Another button with the same text, color, and dimensions should be placed under every product on the page.
Before creating the button, design and requirements documents must be reviewed, and all necessary specifications must be listed down before work begins. This must be done before working on every feature or element on the page so the devs do not miss any guidelines.
What is Validation Testing?
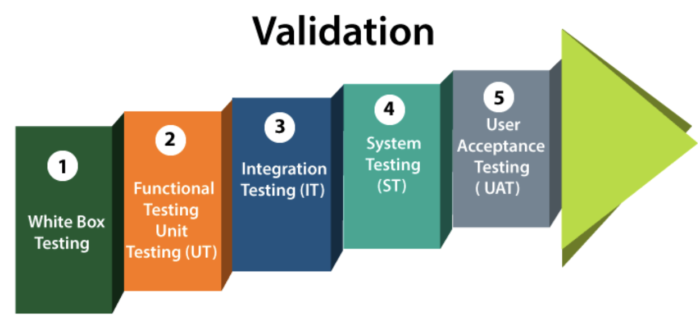
The IEEE-STD-610 defines validation testing as “An activity that ensures that an end product stakeholder’s true needs and expectations are met.”
Unlike verification testing, which occurs at every stage in development, validation testing occurs at the end of a certain module or even after the software has been completely built. Its main intent is to check that the final product matches the stakeholder and customer requirements.
Most forms of QA fall under this category. All tests, from unit tests to User Acceptance Tests, are Validation tests. Some of the common tests under this heading:
Read More: Unit Testing Frameworks in Selenium
All validation tests ensure that a system works as planned by running all its functions and tracking tangible, quantifiable results.
Advantages of Validation Testing
- Any bugs missed during verification will be detected while running validation tests.
- If specifications were incorrect and inadequate from the beginning, validation tests would reveal their inefficacy. Teams will have to spend time and effort fixing them, but it will prevent a bad product from hitting the market.
- Validation tests ensure that the product actually matches and adheres to customer demands, preferences, and expectations under different conditions (slow connectivity, low battery, etc.)
- These tests are also required to ensure that the software functions flawlessly across different browser-device-OS combinations. In other words, it authenticates software for cross browser compatibility. Incase, one is looking for a quick solution to check compatibility on a real device cloud, Try BrowserStack for Free.
When to use Validation Testing
Validation tests must be run after every feature or step in the development process is completed. For example, unit tests, a form of validation tests, are run after every unit of code has been created. Integration tests are run after multiple modules have been completed individually and are ready to be combined.
An important element of validation testing is the running of cross browser testing. QAs must check that every function, feature, and design element appears and functions as expected on different browser-device-os combinations. For example, does the “Add to Cart” button show up and work perfectly on Chrome-Samsung Galaxy A23 and on Safari-iPhone X?
The easiest way to run these tests is to use manual testing and automated testing on a cloud-based testing platform like BrowserStack. Use 3000+ real browsers and devices on the cloud to check every aspect of the software while it is accessed by different devices running various browsers and browsers versions running on different operating systems.
Run Cross Browser Tests on Real Browsers
Verification vs Validation Testing: Differences
Verification TestingValidation TestingIt is the static practice of studying and verifying the specific requirements of a particular stage in development.
It is the dynamic practice of testing the final product after development to check that it meets customer requirements.
It does not require executing code.It always requires executing code.This involves only human verification of required assets.This involves both human and machine-based checking and approval of software.It uses techniques such as document reviews, inspect, product walkthroughs, and desk-checking.It involves various types of product testing – unit tests, integration tests, regression tests, cross browser and cross device testing, etc.It is meant to detect bugs at the beginning of each phase of development.It is meant to detect all bugs that were unnoticed at the verification stage.Its targets are specification documents, the application and software architecture design docs, ER diagrams, database table design, test cases and scenarios, traceability matrix, and the like.Its target is the actual product to be used by the customer after public release.It is undertaken by both developers and testers to ensure that the software adheres to predetermined standards and exactions.It is largely undertaken by experienced Quality Assurance engineers who comb through all features of an application to ensure they work as expected.It comes before validation testing.It follows verification testing.It does not require any devices, platforms, browsers, or operating systems for its execution.It is best executed by using real browsers, devices, and operating systems.
Verification and Validation in Testing are essential concepts that must be meticulously implemented to get the best possible final product. Think of it as two major layers of authentication – both check if the software is built according to plan, one before development starts and one after.
Correctly understanding and utilizing verification and validation testing will go a long way towards filtering out and neutralizing bugs that would otherwise malign user experience and lead to negative reviews and feedback from customers and end-users. Spend a little extra time setting up thorough verification and validation activities, and you won’t have to spend much time dealing with irate users downvoting or abandoning your app.
While performing Validation Test, you can test your application on 3000+ real device-browser combinations by integrating with BrowserStack Automate. This lets you test the application under real user conditions, improving the overall performance and accuracy of the application. BrowserStack Automate also allows you to run parallel tests, thus, optimizing your resources, and accelerating the release time of each build of the application.
Run Tests on Real Device Cloud for Free






