What are the 7 basic quality tools, and how can they change your business for the better?
Reading time: about 7 min
The ability to identify and resolve quality-related issues quickly and efficiently is essential to anyone working in quality assurance or process improvement. But statistical quality control can quickly get complex and unwieldy for the average person, making training and quality assurance more difficult to scale.
Thankfully, engineers have discovered that most quality control problems can be solved by following a few key fundamentals. These fundamentals are called the seven basic tools of quality.
With these basic quality tools in your arsenal, you can easily manage the quality of your product or process, no matter what industry you serve.
Learn about these quality management tools and find templates to start using them quickly.
Mục lục
Where did the quality tools originate?
Kaoru Ishikawa, a Japanese professor of engineering, originally developed the seven quality tools (sometimes called the 7 QC tools) in the 1950s to help workers of various technical backgrounds implement effective quality control measures.
At the time, training programs in statistical quality control were complex and intimidating to workers with non-technical backgrounds. This made it difficult to standardize effective quality control across operations. Companies found that simplifying the training to user-friendly fundamentals—or seven quality tools—ensured better performance at scale
Today, these quality management tools are still considered the gold standard for troubleshooting a variety of quality issues. They’re frequently implemented in conjunction with today’s most widely used process improvement methodologies, including various phases of Six Sigma, TQM, continuous improvement processes, and Lean management.
7 quality tools
1. Stratification
Stratification analysis is a quality assurance tool used to sort data, objects, and people into separate and distinct groups. Separating your data using stratification can help you determine its meaning, revealing patterns that might not otherwise be visible when it’s been lumped together.
Whether you’re looking at equipment, products, shifts, materials, or even days of the week, stratification analysis lets you make sense of your data before, during, and after its collection.
To get the most out of the stratification process, consider which information about your data’s sources may affect the end results of your data analysis. Make sure to set up your data collection so that that information is included.
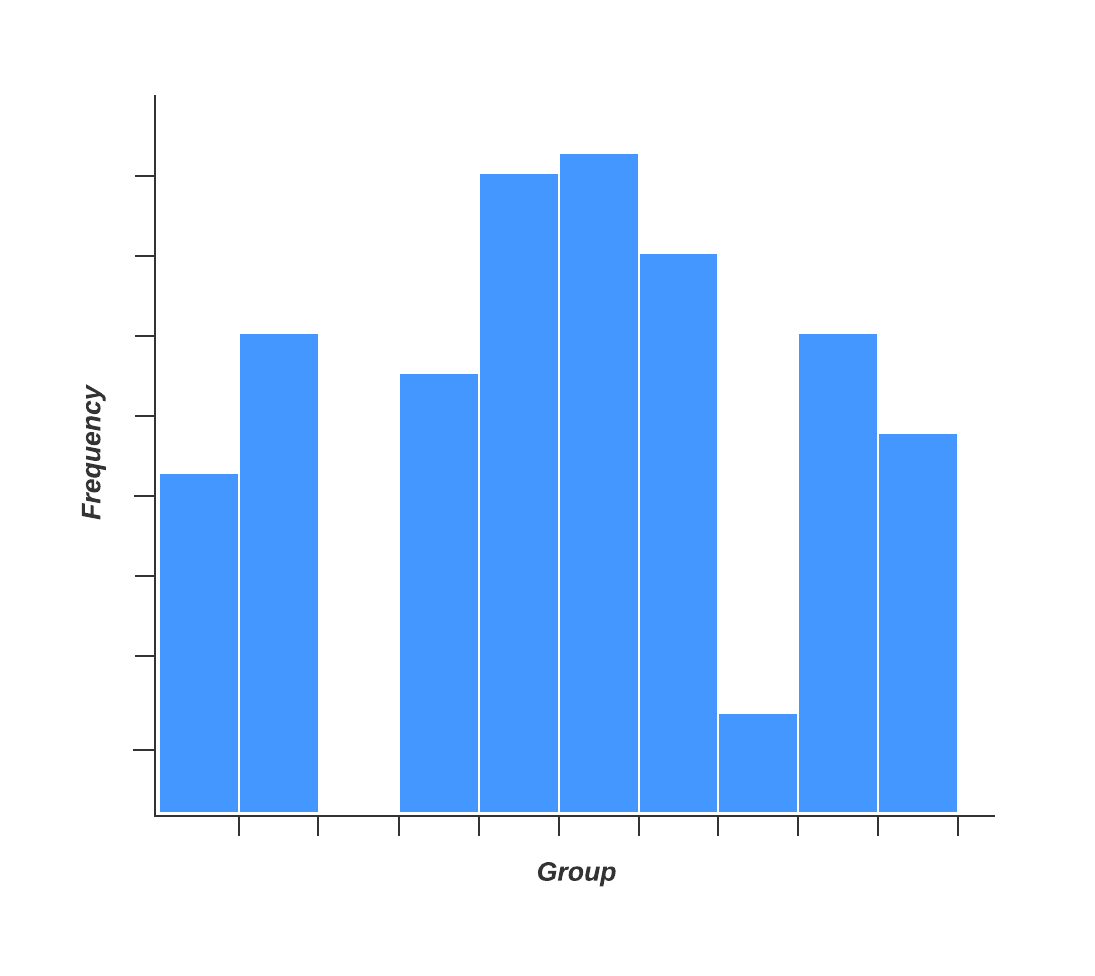
2. Histogram
Quality professionals are often tasked with analyzing and interpreting the behavior of different groups of data in an effort to manage quality. This is where quality control tools like the histogram come into play.
The histogram represents frequency distribution of data clearly and concisely amongst different groups of a sample, allowing you to quickly and easily identify areas of improvement within your processes. With a structure similar to a bar graph, each bar within a histogram represents a group, while the height of the bar represents the frequency of data within that group.
Histograms are particularly helpful when breaking down the frequency of your data into categories such as age, days of the week, physical measurements, or any other category that can be listed in chronological or numerical order.
3. Check sheet (or tally sheet)
Check sheets can be used to collect quantitative or qualitative data. When used to collect quantitative data, they can be called a tally sheet. A check sheet collects data in the form of check or tally marks that indicate how many times a particular value has occurred, allowing you to quickly zero in on defects or errors within your process or product, defect patterns, and even causes of specific defects.
With its simple setup and easy-to-read graphics, check sheets make it easy to record preliminary frequency distribution data when measuring out processes. This particular graphic can be used as a preliminary data collection tool when creating histograms, bar graphs, and other quality tools.






