What is Quality Function Deployment (QFD)? Definition, Process, House of Quality Example, Benefits, Disadvantages – The Investors Book
Definition: Quality function deployment is a systematic approach of specifying the customer needs and desires, rating them in terms of priority and designing the quality products and process to serve these requirements, through proper planning.
QFD is a process of bridging the gap between where we stand and what we aim at, by providing target values and competitive analysis.
This tool is widely applied in case of:
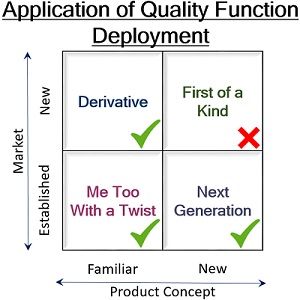
- Derivative products which are familiar but launched in a new market
- Products which are casual but have been introduced with a twist;
- Next-generation products which have a new concept and started in an established market.
However, QFD is not applicable in case of products which have a new concept and introduced in a new market (i.e., first of its kind products). This is because of insufficient information or consumer data.
Mục lục
Content: Quality Function Deployment (QFD)
QFD Process
A quality function deployment emphasizes on product and process design. It involves the following four phases:
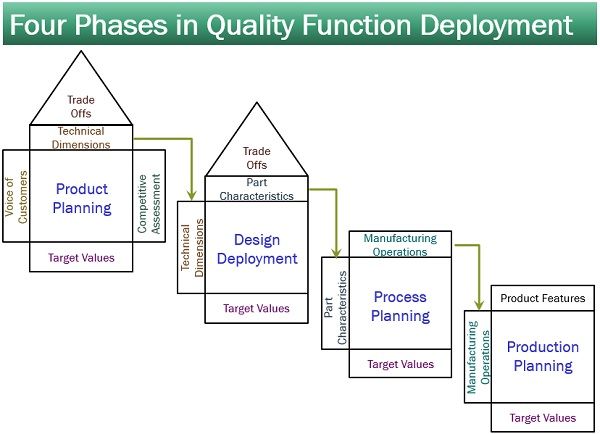
Phase 1: Product Planning
The initial step of QFD exercise involves product planning. It is a process of analyzing the customer requirements and comparing these with the product’s technical specifications to ensure quality optimization while designing a product. It involves the creation of the house of quality for a particular product.
House of Quality
House of quality is a matrix which is the basis of product planning, and its diagram looks like a house. It is a realistic approach which analyzes the consumer desires and matches it with the technical attributes of a product, to optimally fulfil these requirements by utilizing the resources available with the organization.
This matrix determines the following parameters:
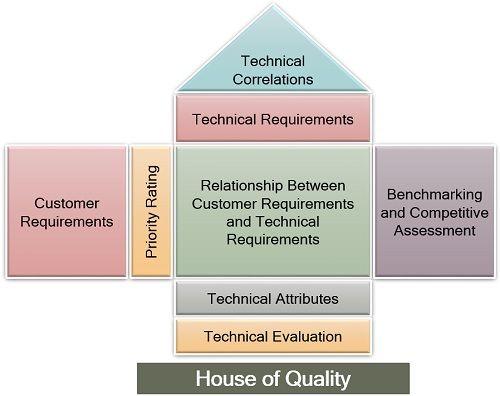
- Customer needs or requirements;
- Product design to suit these needs and wants;
- The priority of each item and its importance while designing a product and process;
- Competitive assessment and analysis of each element;
- Establishing benchmarks and target values for each component.
The above diagram gives an overview of the different sections of a house of quality matrix.
Phase 2: Design Deployment
At this stage, the product design is developed by identifying the suitable assemblies or systems, sub-systems and components.
Following are the various levels analyzed at this phase:
- System Level: It includes the analysis of technical requirements for a product, prioritization of these specifications and their impact over a particular system or assembly.
- Sub-system Level: The complex systems are then distributed into sub-systems to list, rank and study the critical components.
- Component Level: The characteristics are then figured out in terms of purchased components, thus provides as a source of information to the suppliers.
Phase 3: Process Planning
Now comes the process development stage of QFD. This phase evaluates the correlation between the various processes or steps and the technical and functional specification of the product. It helps to identify the process which meets the part requirements in the best possible manner.
Following functions are performed in this stage:
- Analyze the crucial processes;
- Identify the process flow;
- Find out the need for production equipment;
- Develop the framework for a critical process.
Phase 4: Production Planning
It is the last phase of quality function deployment. At this stage, the product’s quality control throughout the production process is determined.
In other words, quality targets are decided during production planning. The various related activities carried out are as follows:
- Examine the crucial technical and process characteristics;
- Identify methods of process control;
- Analysis and testing of the process and associated parameters.
House of Quality Example
To have a clear understanding of the house of quality, let us study the given an example:
XYZ company is the manufacturer of helmets. It conducted the quality function deployment to review the customer requirements, technical attributes, target values, competitiveness and measures for enhancing the product and process quality.
The company faced competition from the three major market players, ABC, LMN and PQR.
Given below is the house of quality of XYZ helmets:
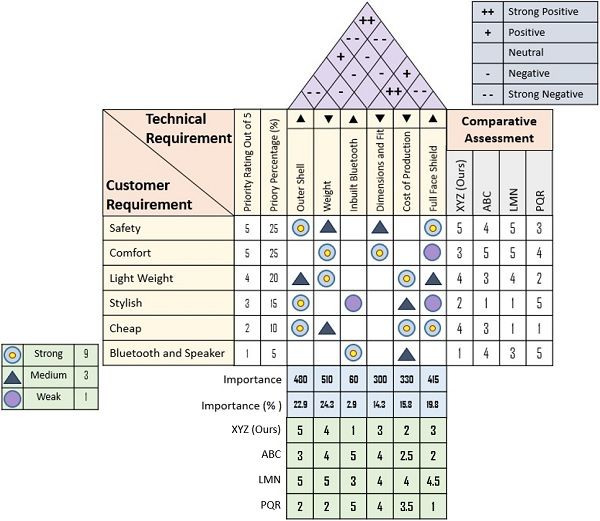
- The middle part of the matric presents the relationship between customer needs and the technical specifications of the product.
- The roof of the house shows the correlation between the technical specifications.
- The bottom of the matrix depicts the importance of each technical specification when compared to consumer needs.
- The columns below the importance (%) shows the ratings in terms of fulfilment of the individual technical requirement by each company.
- The right side of the matrix provides a comparative study by listing the customer preference ratings for the brands in terms of individual requirements.
From the above diagram, we can quickly figure out that:
- The company has met the safety requirements of the customers to the fullest. However, it needs to work more on the styling of its products.
- Also, XYZ helmet’s outer shell is considered to be of premium quality and robust build. But, the company has to control its cost of production.
- Moreover, the company has the edge over the other brands in terms of safety, price and light weightedness.
- The company has to pay attention to the comfort level of the helmets still to improve consumer satisfaction.
Benefits of QFD
The quality function deployment is the task of design engineers; however, the efforts of all the departments are required to implement it successfully.
Let us now understand the various advantages QFD has in an organization:
Improves Product Quality: QFD is a tool used by the companies engaged in the manufacturing and production of goods or services to continually enhance the quality of their products.
Systematic Information: Designing the house of quality for a particular product enables the organization to arrange the data obtained, in an orderly manner.
Competitive Quality Analysis: It also determines the competitiveness of the firm through quality analysis on the grounds of customer reviews and preference.
Reduces Wastage: QFD directs the efforts of the organization’s personnel in the right direction and thus reduces the chances of wastage of time, efforts and resources.
Increases Customer Satisfaction: It ensures better quality products by analyzing consumer preference, thus enhancing the level of customer satisfaction.
Shortens Product Development Cycle: With the help of continual research and improvement of product quality, the product development cycle becomes abridged and leads to the sustainability of the organization in the market.
Unanimous Decision: QFD is a team-oriented activity; therefore, the product-related decisions so are taken have the consent of all the members involved in the process.
Decreases Startup Cost: It reduces a startup’s expenses tremendously since it is a cost-efficient means of product design and marketing research.
Promotes Team Work: It is a complex process and cannot be performed single-handedly. Thus, it requires the efforts of the whole team, including the personnel from different departments such as marketing, production, research and finance departments.
Disadvantages of QFD
Though QFD is an essential tool for product design and quality analysis, it has certain drawbacks, which makes it ineffective for some organizations. Following are some of these shortcomings:

The ambiguity of Categories: The customer requirement categories are based on qualitative aspects and therefore appears to be vague and not very clear at times.
Complex Matrix: The house of quality is compiled of a matrix, and in the condition of multiple categories and technical elements, this matrix becomes convoluted and difficult to analyze.
The difference of Opinion: Different team members can have varying opinions, which may lead to arguments and indecisiveness.
Not Universally Applicable: The QFD technique cannot be applied in the case of customized products and valuables like antique items. Also, the products which have a limited number of consumers cannot be analyzed through this tool.
Labour-Intensive Process: It requires team building, i.e., the involvement of various personnel of the organization, which ultimately increases the non-productive time.
Comprehensive and Extensive Method: QFD involves making of a matrix which is elaborated holistically. Compiling all this information in a single house of quality makes the diagram quite lengthy and broad, which may lead to confusion and misunderstanding.
Time Consuming: The process of data collection and its presentation on a house of quality consumes a lot of time and efforts of the personnel.
Based on Qualitative Data: The results so obtained cannot be termed as accurate since they are based on the qualitative input rather than quantitative information.
Conclusion
Quality function deployment is a six sigma strategy which considers quality as the primary parameter for customer satisfaction.
Planning is the base for building up a strong brand and brand image. Therefore, QFD is an inevitable part of the manufacturing and production organizations.






