H.264 vs. H.265: Video codecs compared
Codecs 101
It’s a term you’ll hear often in the streaming world and probably use a fair bit yourself. But what even is a “codec”?
A video codec is a process for compressing and decompressing video data. There are also audio codecs that do the same for audio. The term itself is a combination of the words “coding” and “decoding.”
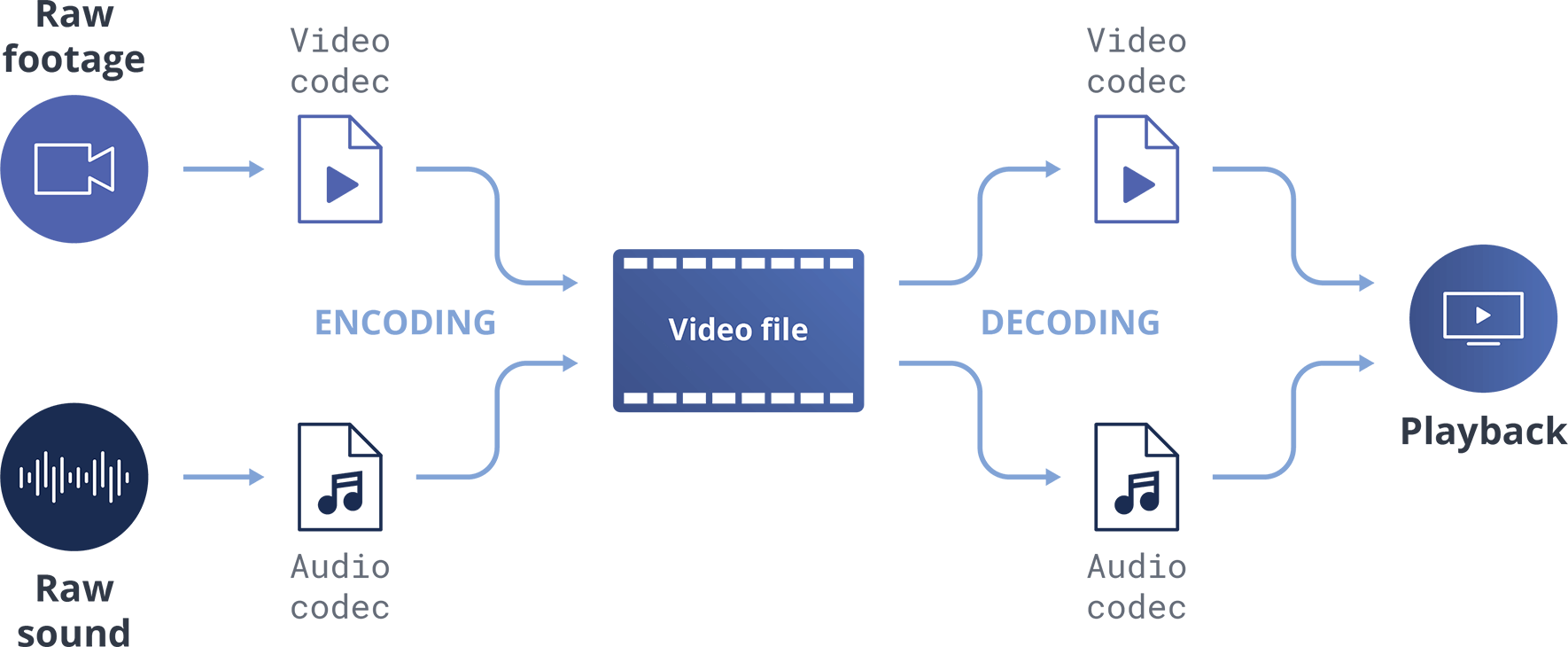
Codecs are often confused with containers. For video files, that means formats like AVI, MOV, or MP4. The difference is this: A container holds the compressed video and audio and any other components of the file, such as any metadata or subtitles. The codec comes into play at the start, determining how the raw footage and sound are compressed within the container, and decodes the file for playback as needed.
There are lots of different video codecs out there. MPEG-2, JPEG2000, and VP9 are just a few you might hear about. But out of all of them, H.264 and H.265 get the most attention by far.
Codecs come in two classes: lossless and lossy. During playback, lossless codecs completely reconstruct the compressed data while lossy codecs serve up only an approximation. It’s a trade-off between quality and playback experience, with lossy codecs offering much smoother playback that might include interpolation and other compression artifacts. Streaming lossless media isn’t feasible for most Internet connections, which is why lossy codecs like H.264 and H.265 prevail online.






