Software Engineering | Software Characteristics – GeeksforGeeks
Software is defined as a collection of computer programs, procedures, rules, and data. Software Characteristics are classified into six major components:
Software engineering is the process of designing, developing, testing, and maintaining software. The characteristics of software include:
- It is intangible, meaning it cannot be seen or touched.
- It is non-perishable, meaning it does not degrade over time.
- It is easy to replicate, meaning it can be copied and distributed easily.
- It can be complex, meaning it can have many interrelated parts and features.
- It can be difficult to understand and modify, especially for large and complex systems.
- It can be affected by changing requirements, meaning it may need to be updated or modified as the needs of users change.
- It can be affected by bugs and other issues, meaning it may need to be tested and debugged to ensure it works as intended.
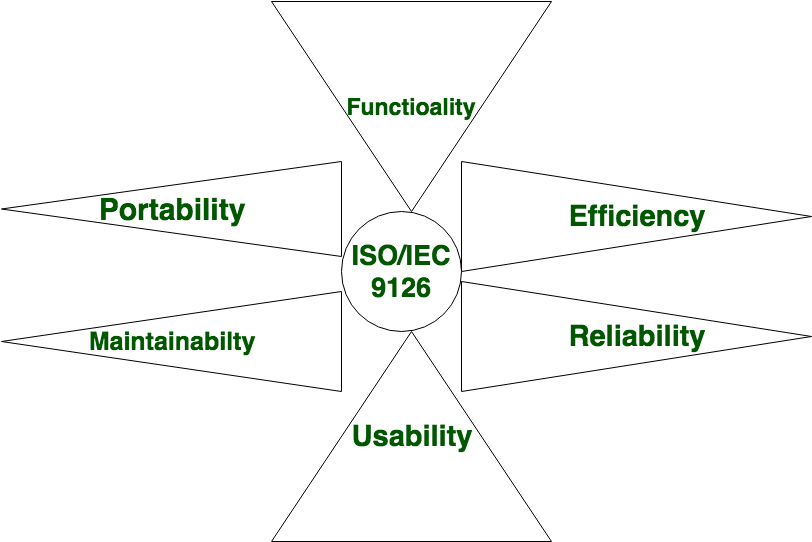
These components are described below:
- Functionality:
It refers to the degree of performance of the software against its intended purpose.
Functionality refers to the set of features and capabilities that a software program or system provides to its users. It is one of the most important characteristics of software, as it determines the usefulness of the software for the intended purpose. Examples of functionality in software include:
- Data storage and retrieval
- Data processing and manipulation
- User interface and navigation
- Communication and networking
- Security and access control
- Reporting and visualization
- Automation and scripting
The more functionality a software has, the more powerful and versatile it is, but also the more complex it can be. It is important to balance the need for functionality with the need for ease of use, maintainability, and scalability.
Required functions are:

- Reliability:
A set of attributes that bears on the capability of software to maintain its level of performance under the given condition for a stated period of time.
Reliability is a characteristic of software that refers to its ability to perform its intended functions correctly and consistently over time. Reliability is an important aspect of software quality, as it helps ensure that the software will work correctly and not fail unexpectedly.
Examples of factors that can affect the reliability of software include:
- Bugs and errors in the code
- Lack of testing and validation
- Poorly designed algorithms and data structures
- Inadequate error handling and recovery
- Incompatibilities with other software or hardware
To improve the reliability of software, various techniques and methodologies can be used, such as testing and validation, formal verification, and fault tolerance.
A software is considered reliable when the probability of it failing is low and it is able to recover from the failure quickly, if any.
Required functions are:
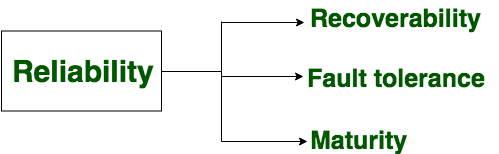
- Efficiency:
It refers to the ability of the software to use system resources in the most effective and efficient manner. The software should make effective use of storage space and executive command as per desired timing requirements.
Efficiency is a characteristic of software that refers to its ability to use resources such as memory, processing power, and network bandwidth in an optimal way. High efficiency means that a software program can perform its intended functions quickly and with minimal use of resources, while low efficiency means that a software program may be slow or consume excessive resources.
Examples of factors that can affect the efficiency of software include:
- Poorly designed algorithms and data structures
- Inefficient use of memory and processing power
- High network latency or bandwidth usage
- Unnecessary processing or computation
- Unoptimized code
To improve the efficiency of software, various techniques and methodologies can be used, such as performance analysis, optimization, and profiling.
Efficiency is important in software systems that are resource-constrained, high-performance, and real-time systems. It is also important in systems that need to handle a large number of users or transactions simultaneously.
Required functions are:

- Usability:
It refers to the extent to which the software can be used with ease. the amount of effort or time required to learn how to use the software.Required functions are:

- Maintainability:
It refers to the ease with which the modifications can be made in a software system to extend its functionality, improve its performance, or correct errors.Required functions are:

- Portability:
A set of attributes that bears on the ability of software to be transferred from one environment to another, without or minimum changes.Required functions are:

Apart from above mention qualities of software, there are various characteristics of software in software engineering:
- Software is developed or engineered; it is not manufactured in the classical sense:
- Although some similarities exist between software development and hardware manufacturing, few activities are fundamentally different.
- In both activities, high quality is achieved through good design, but the manufacturing phase for hardware can introduce quality problems than software.
- The software doesn’t “wear out.”:
- Hardware components suffer from the growing effects of many other environmental factors. Stated simply, the hardware begins to wear out.
- Software is not susceptible to the environmental maladies that cause hardware to wear out.
- When a hardware component wears out, it is replaced by a spare part.
- There are no software spare parts.
- Every software failure indicates an error in design or in the process through which design was translated into machine-executable code. Therefore, the software maintenance tasks that accommodate requests for change involve considerably more complexity than hardware maintenance. However, the implication is clear—the software doesn’t wear out. But it does deteriorate.
- The software continues to be custom-built:
- A software part should be planned and carried out with the goal that it tends to be reused in various projects.
- Current reusable segments encapsulate the two information and the preparation that is applied to the information, empowering the programmer to make new applications from reusable parts.
- In the hardware world, component reuse is a natural part of the engineering process.
My Personal Notes
arrow_drop_up





