The 3 Best Ways To Resize An Image In Photoshop (Easy!)
Mục lục
How To Resize An Image Or Layer In Photoshop
Whether you need to fit your photo to a certain dimension or rescale a layer to fit your project, learning how to resize an image in Photoshop is important. There are a few different ways that you can do it, but some will leave you will a lower quality image than what you started.
To ensure you maintain the same high-res quality that you started with make sure to follow three of the best methods outlined below.
3 Ways Resize Images Without Losing Quality
Below are three of the best ways to resize an image in Photoshop without losing quality. Whether you want to rescale an entire image or just make a layer bigger, these options make it easy.
1. The Image Size Adjustment
The Image resize adjustment lets you change the dimensions and resolution of a photo. If you have specific dimensions you need to match, this method is very effective. Especially if you’re trying to print a photo, you can directly alter the image size to get the best results.
Here’s how to do it:
Step 1: Go To Image > Image Size
With the layer, you want to make bigger selected, go up to Image > Image size.
Alternatively, you can use the keyboard shortcut Option + Command + I (Mac) or Alt + Control + I (PC) to access the same tool.
Step 2: Set Your New Image Dimensions
In the Image Size dialogue box, there are a few different options to work with. The first one to look at is your image’s current dimensions.
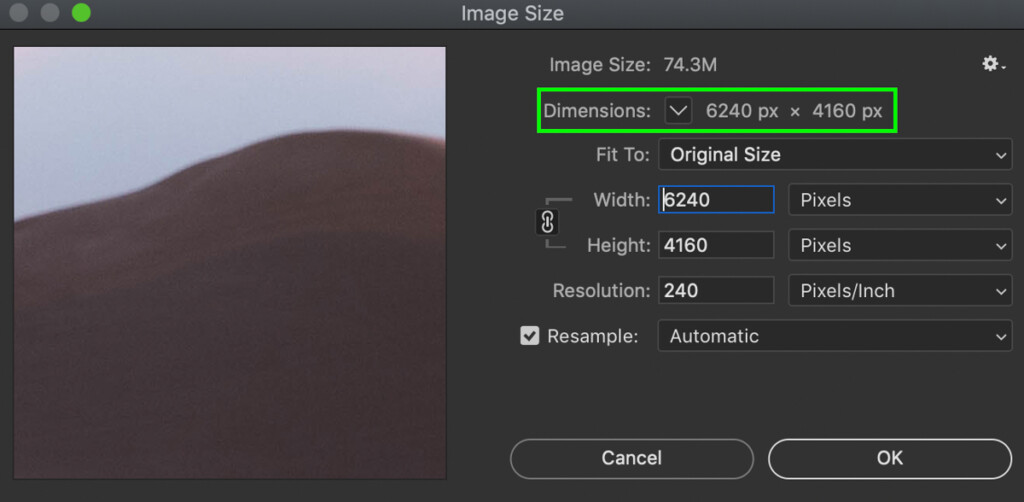
Located near the top of the window, you can change the dimension measurements by clicking on the drop-down menu.

This can be useful if you have an easier time visualizing image size with a different kind of measurement. After all, it’s easier to imagine the size of a 4×2″ rectangle than a 1920×1080 pixel image.
Below that, you’ll find the width and height options. By default, they’ll be set to match the current size of your image. However, they can be adjusted to whatever image size you’re going for.
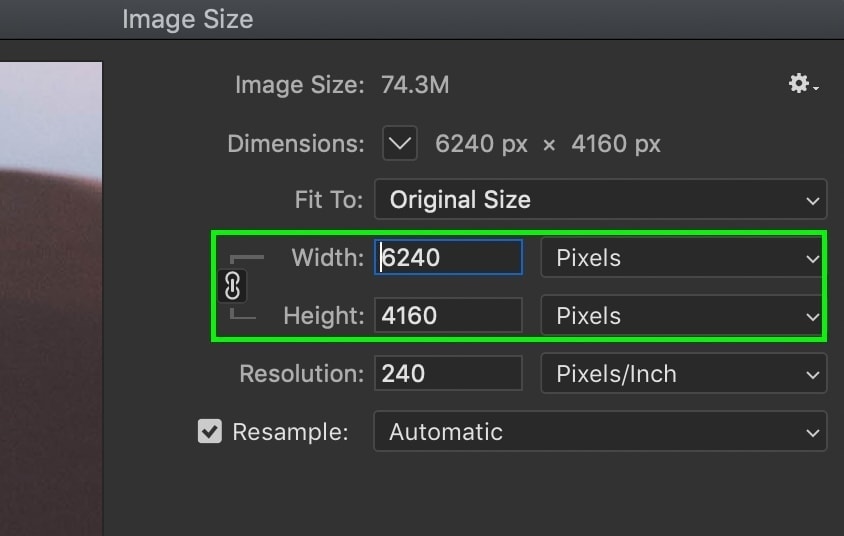
To edit them, simply click on the width or height value, and type in a new dimension.
If you’re trying to resize your photo for print, it can be useful to change the dimension value to inches or centimeters. That way, if you’re trying to print an 8×10 inch photo, you can type in those exact dimensions.
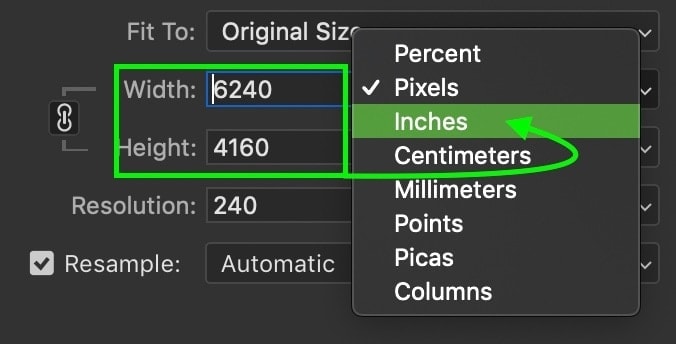
This just makes it a heck of a lot easier to get accurate sizing when you scale your photo.
Now sometimes, you may not want to keep the same aspect ratio that you started with. In that case, you’ll want to click on the chainlink icon beside the dimension values.
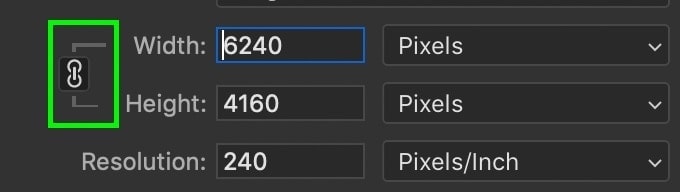
With your width and height unlinked, they can be adjusted independently. Otherwise, they’ll automatically be adjusted to match the original aspect ratio of your photo.

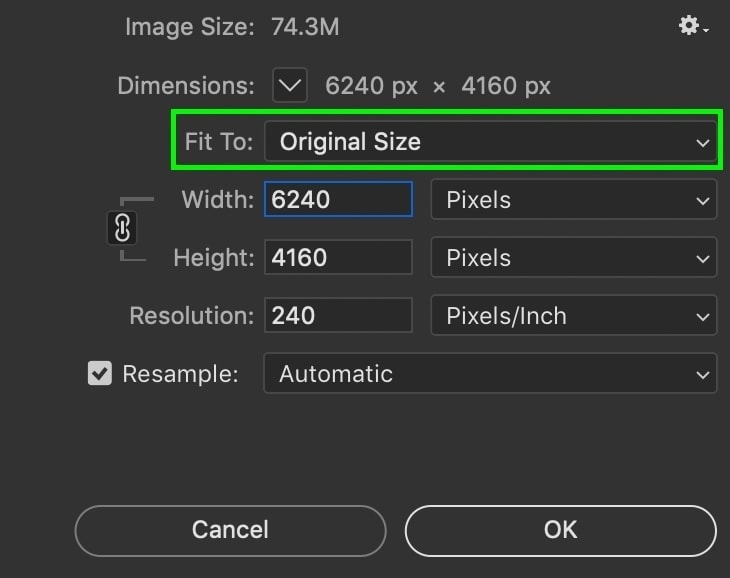
Lastly, you can choose from various preset image dimensions and resolutions via the Fit To option.

Step 3: Change Your Image Resolution
With your image dimensions enlarged, it’s time to change the resolution. In simple terms, a higher resolution will give you more pixels in your image, which ultimately creates a higher quality and more crisp looking photo.
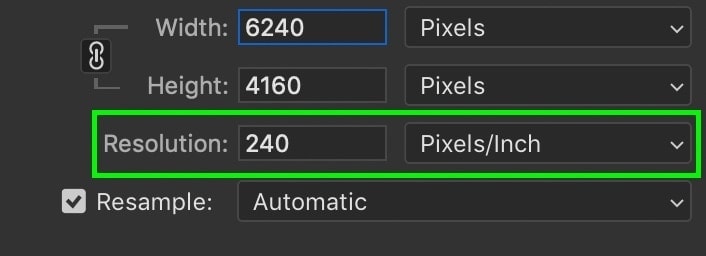
There are two different ways you can set the resolution, which is in PPI (Pixels Per Inch) or PPC (Pixels Per Centimeter).
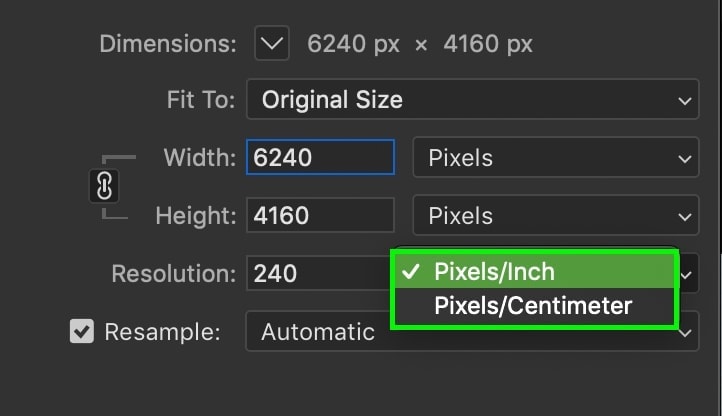
It doesn’t really matter which resolution measurement you use. Just be aware of this setting if you’re trying to match specific image specs.
To increase the resolution of your photo, simply type in a new resolution value.
From there, make sure the resample option is checked off and set to Automatic.
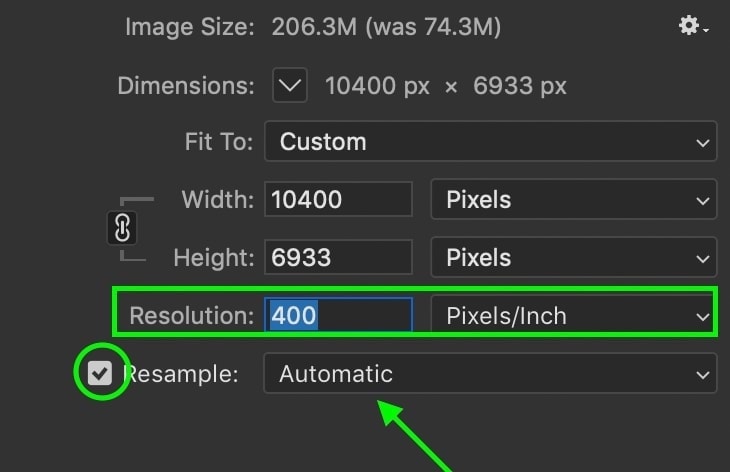
This setting ensures your photo maintains its quality, even if you’re making the dimensions significantly bigger.
Step 4: Apply Your Resize Settings To The Photo
With all your settings good to go, just press OK at the bottom of the Image Size dialogue box.
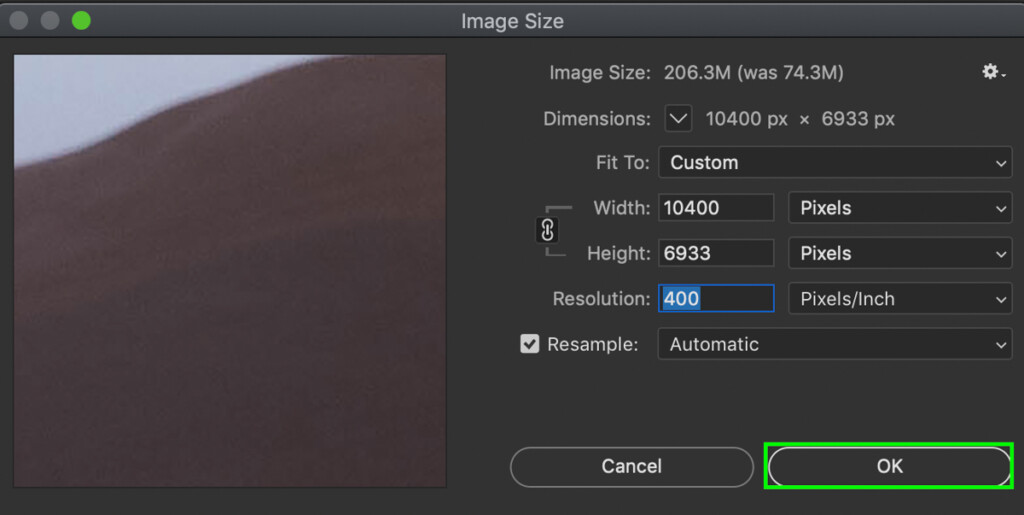
Depending on how drastic your enlargements were, Photoshop may take a minute to apply your effects.
Once complete, your image will increase in size to match the dimensions and resolution you set earlier.

This method is one of the fastest ways to resize an image while ensuring you don’t lose image quality.
– Using Smart Objects
Now the previous method enlarged a single layer within its own project. So what if you want to resize a layer that can still be freely moved between Photoshop documents?
Well, that’s where smart objects come into play.
Smart objects are a way to resize layers in Photoshop without losing any quality. Since they place your image into a “container,” you only ever edit the container and not the actual image.
So even if you were to scale up and down a layer over and over, you would maintain the same consistent quality. With raster layers, you’d end up with a pixelated, low-resolution mess.
You can learn how smart objects work more in-depth in this post.
For now, let’s continue and learn how to use smart objects to enlarge a layer.
Step 1: Convert Your Layer Into A Smart Object
Before you adjust your layer, you need to first convert it into a smart object. With your desired layer selected, simply right-click and choose Convert To Smart Object.

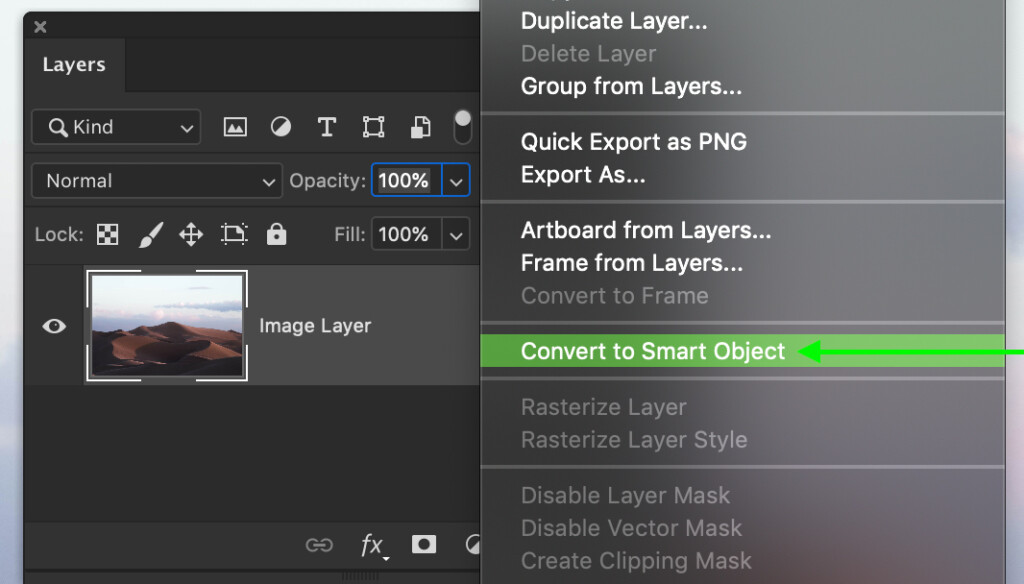
You’ll know your layer is a smart object from the smart object icon over your layer’s thumbnail.

Step 2: Resize Your Layer With The Transform Tool
To adjust your layer’s size, press Command + T (Mac) or Control + T (PC) with your smart object layer selected.
Clicking on any corner of the transform box, you can scale your image to fit your needs.

If you need to move it into another document, just select the Move Tool and drag and drop it into your other project.

With two simple steps, you can quickly make your photo bigger or move it between projects. The only downside to this method is that you cannot control the exact dimensions of the photo.
However, if you’re working on a canvas with particular image dimensions, using smart objects is a great way to make your photo fit on the canvas. Best of all, it guarantees you keep the highest image quality, no matter how much you scale the layer.
– Drag & Drop From Your Computer
For the third way to resize images without losing quality, all you have to do is drag and drop them from your computer. When you drag and drop files, Photoshop allows you to automatically reposition and scale the layer.
After you commit to your changes, the layer is converted to a smart object and maintains its original image quality. If you want a more direct way of scaling images and layers, then this method is for you.
Step 1: Select A File From Your Computer
With Photoshop already open, locate the file you want to work with on your computer.

Step 2: Drag And Drop The File Into Photoshop
With your desired image selected, just click and drag it onto your Photoshop document. This will automatically import it into your Photoshop document and let you begin to work on the photo.
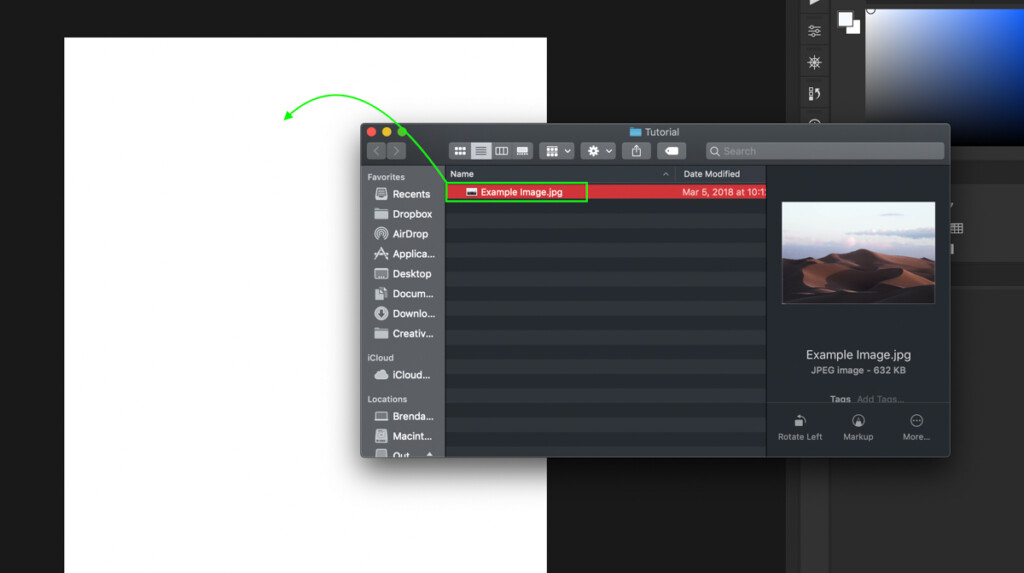
Step 3: Resize Your Image To Fit Your Canvas
When you first import the photo, you’ll notice a transform box around the image. That means you can adjust the size of your layer as needed.

For this example, I want to fill my entire canvas with the photo, so I’ll click on the corner and drag it out accordingly.

Since the image isn’t officially placed, you don’t have to worry about converting it to a smart object quite yet.
Step 4: Commit To Your Changes
With your image in the correct position, hit the check box at the top of your screen to commit to the changes. You can also press the Enter Key on your keyboard instead.
Now your scaling adjustments will be applied, and your new layer will be shown as a smart object in your layers panel.

If you need to make further adjustments to the layer’s size, simply select the layer and grab the Move Tool by pressing V. From there, you’ll be able to change the size and position of your layer.
How To Resize Your Canvas In Photoshop
Now that you know the three best ways to resize images in Photoshop without losing quality let’s talk about your canvas. In some cases, you’ll want to resize your entire canvas rather than a particular layer. Luckily this is very simple to do.
First, go up to Image > Canvas Size.
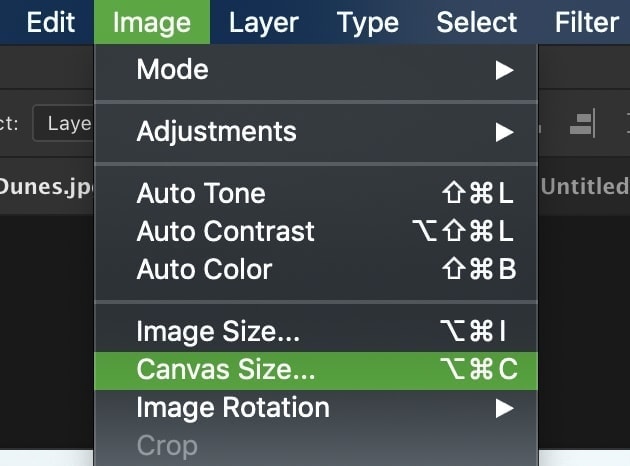
In the Canvas Size dialogue box, you’ll have two dimension values to set. Just like with resizing the image, you can directly input the new dimensions you want.
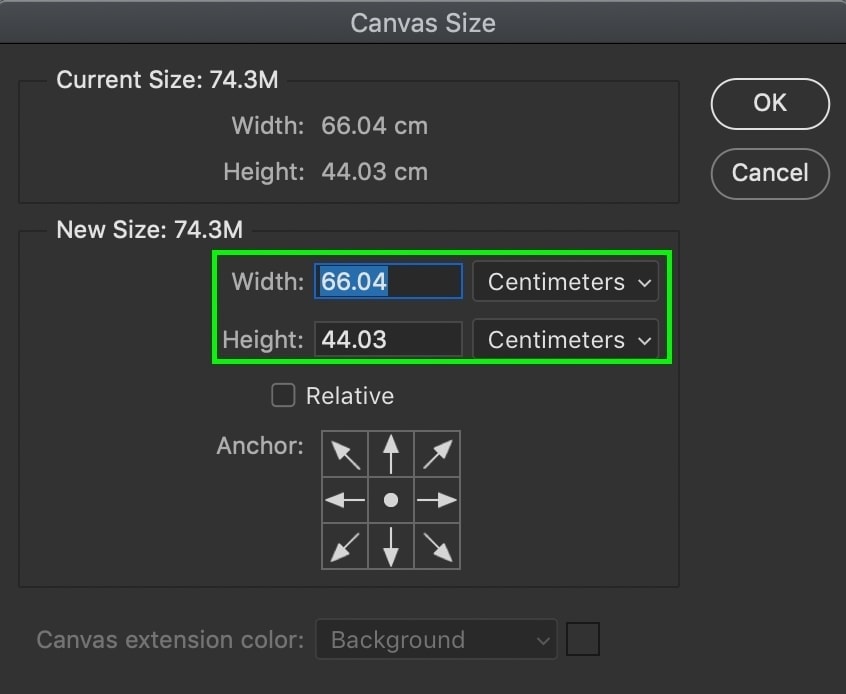
You can also change the measurement type via the drop-down menu beside the dimension values if need be.
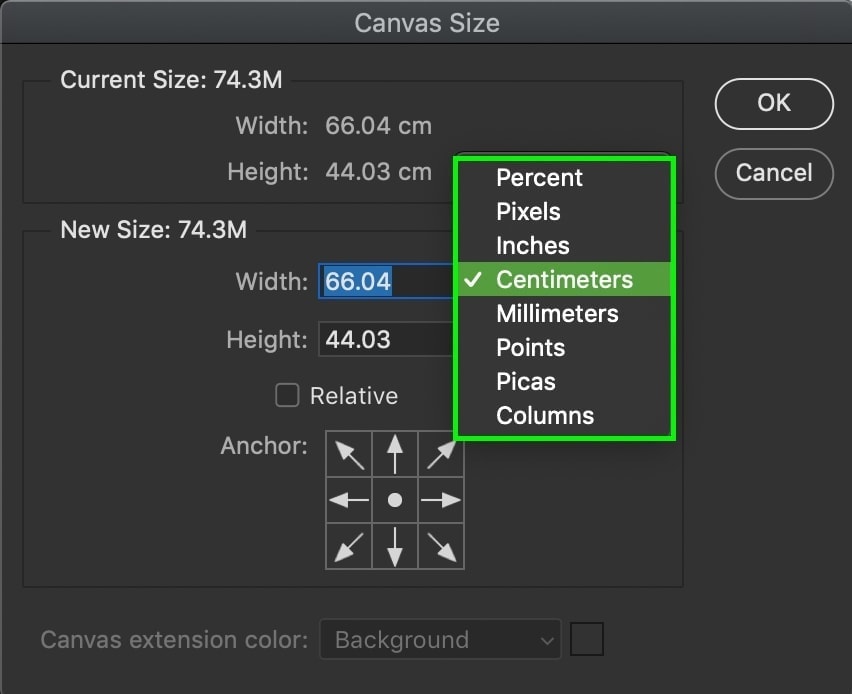
Below the dimensions is an Anchor setting that lets you choose how your canvas is enlarged. By default, it is set to the middle, which means all sides of your canvas will be expanded equally.
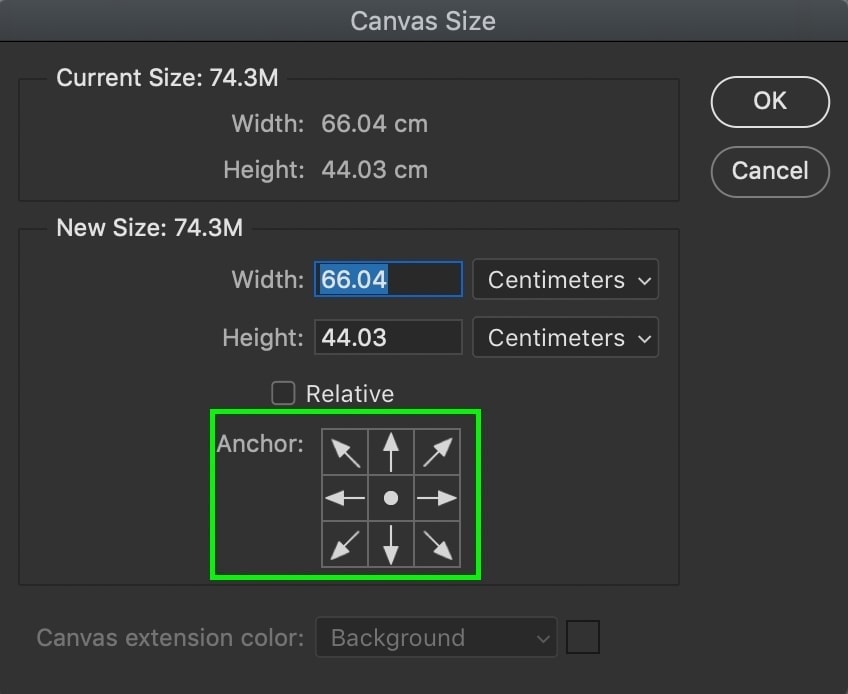
However, let’s say I want to extend my canvas vertically, but only in the upward direction. I would set my anchor point to the bottom middle and adjust the height value accordingly.
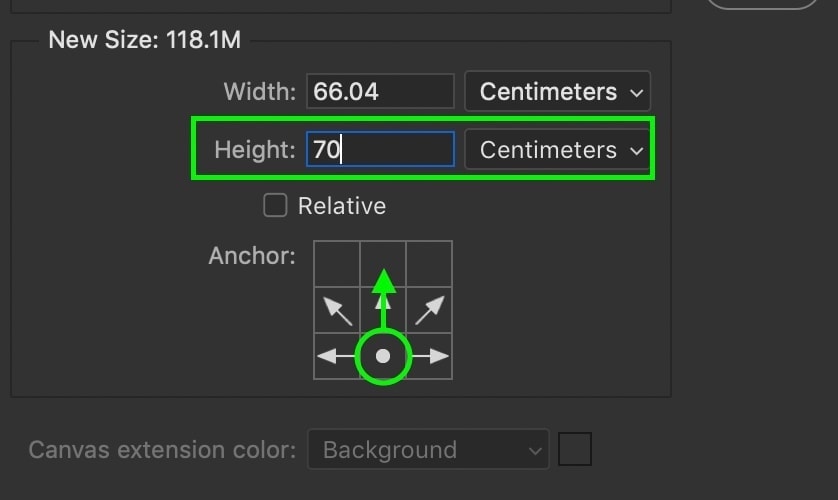
Now when I commit to the changes, the canvas will only extend from the upper area rather than the bottom.
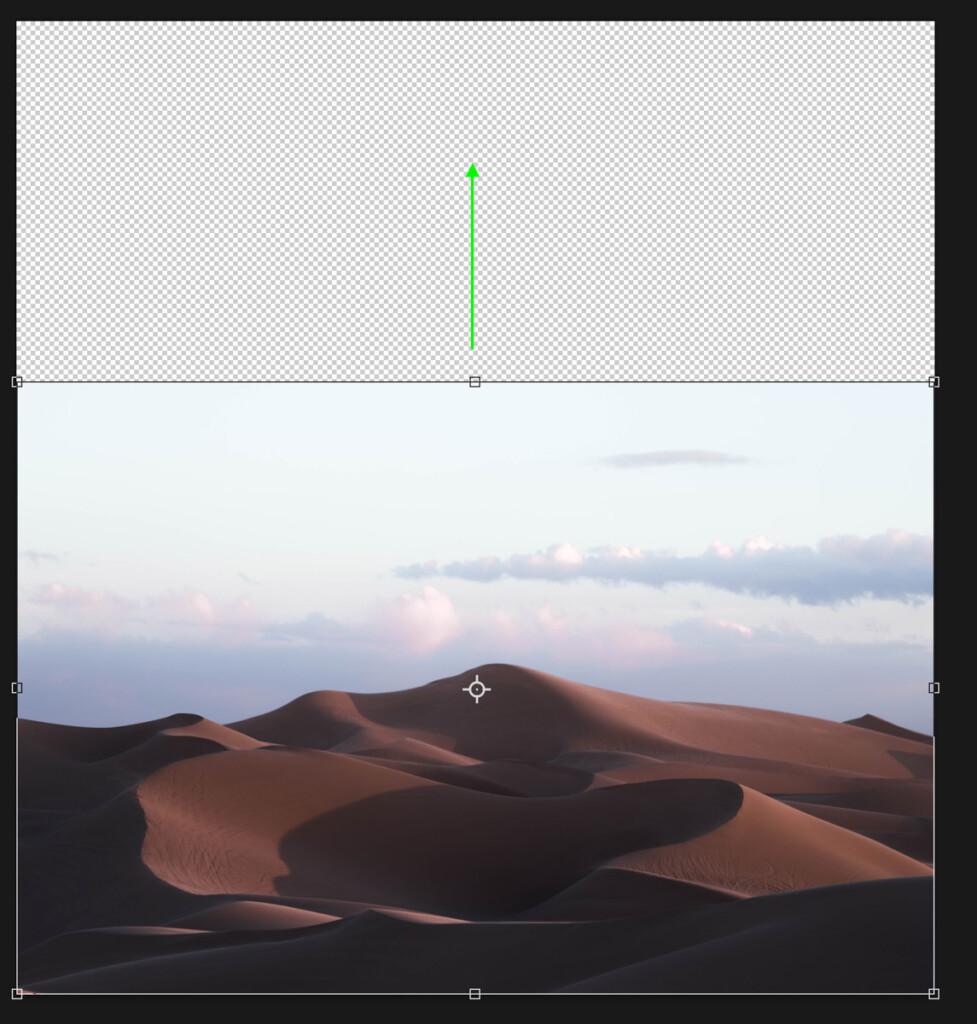
The anchor point isn’t always necessary but can be a helpful option if the opportunity arises. So it’s worth keeping in mind!
How To Resize An Image By Dragging
To resize a layer by dragging, select the Move Tool (V) and click on the layer you want to adjust. A transform box will appear around your layer, which you can click and drag the edges of. As you drag out the corners, you’ll be able to resize your layer as needed.

With that said, it’s important to remember that you may lose quality if you don’t first convert your layer to a smart object. If you resize a rasterized layer, you’ll gradually lose quality as you adjust the size of the layer.

So before you significantly resize a layer by dragging with the Move Tool, make sure you are working with a smart object!
How To Stretch An Image When You Resize
To scale and stretch an image, there are a few easy shortcuts you can use. With your layer highlighted, select the Move Tool and click on any edge of the layers transform box. Holding the Alt or Option key while scaling can stretch your layer horizontally or vertically.

This method will synchronize the stretch adjustments to both sides of your photo.
So now you know a few different ways to resize an image in Photoshop without losing quality, plus additional tips to make photos bigger with ease. These are some of my favorite way of changing the size of images and layers in Photoshop, and some tend to be faster than others. Try experimenting with each of these options and see which one works best for you!
Happy Editing,
– Brendan 🙂






