TQM in CQM for Construction Quality – Construction Quality Management
Total Quality Management or TQM is one of the sets of tools and techniques used in CQM Methodology for Construction Quality as one of many Best Practices integrated into the CQM Framework for the most innovative and LEAN method of Apply CQM for every organization and Construction Project.

In 1984, the US Navy asked quality consultants and researchers to assess statistical process control and to make recommendations as to how to apply their approaches to improve the Navy’s operational effectiveness. Edwards Deming’s teachings and approach to Quality Management was adopted and Navy branded the effort “Total Quality Management” in 1985.
Later with the creation of the Federal Quality Institute in 1988, the TQM was adopted by many elements of government and the armed forces, including the US Department of Defense, the United States Army, US Coast Guard, and US Environmental Protection Agency.
The private sector followed suit, flocking to TQM principles not only as a means to recapture market share from the Japanese, but also to remain competitive when bidding for contracts from the Federal Government since “total quality” requires involving suppliers, not just employees, in process improvement efforts. Source: Wikipedia.org
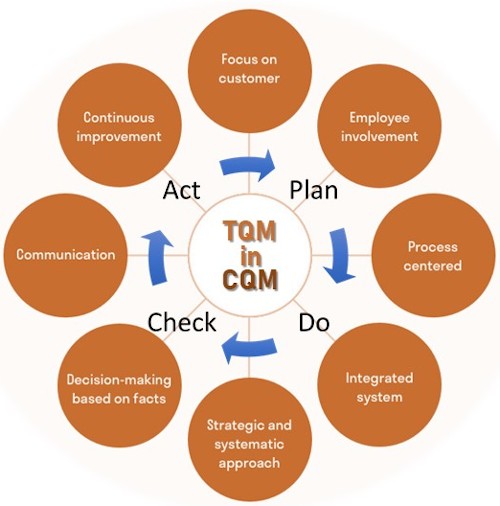
TQM PDCA, 6 C’s, and 8 Pillars
Deming’s TQM has few principles and pillars that have become the benchmark for many other integrated systems. PDCA cycle or Plan-Do-Check-Act continuous improvement model is one of many TQM methodologies that have been adopted by other systems such as PMBoK Framework.
CQM use of TQM for Construction Quality is also benefiting from this Best Practices by applying an Integrated Continous Improvement System based on the following 6 C’s of TQM:
- Commitment from Employees
- Quality Improvement Culture
- Continuous Improvement
- Cooperation from Employees
- Focus on Customer Requirements
- Effective Control
However, CQM Expert Dr. Hani Emari, PMP has modified the PDCA by applying the third dimension view of decreasing cycle as time passes by to illustrate the less effort and time required to pass each cycle to the next elevated step as the organization reaches Maturity in its Continuous Improvement methodology. The model is created by Ms. Hana Emari a blender modeler artist as follows:
TQM Deming 14 Points
Deming’s 14 Points on Quality Management, or the Deming Model of Quality Management, a core concept on implementing total quality management (TQM), is a set of management practices to help companies increase their quality and productivity.
Deming’s 14 Points for Total Quality Management
- Create constancy of purpose for improving products and services.
- Adopt the new philosophy.
- Cease dependence on inspection to achieve quality.
- End the practice of awarding business on price alone; instead, minimize total cost by working with a single supplier.
- Improve constantly and forever every process for planning, production and service.
- Institute training on the job.
- Adopt and institute leadership.
- Drive out fear.
- Break down barriers between staff areas.
- Eliminate slogans, exhortations and targets for the workforce.
- Eliminate numerical quotas for the workforce and numerical goals for management.
- Remove barriers that rob people of pride of workmanship, and eliminate the annual rating or merit system.
- Institute a vigorous program of education and self-improvement for everyone.
- Put everybody in the company to work accomplishing the transformation.
CQM use of TQM
The CQM Methodology uses TQM’s Principles and adds more to it by adopting principles from the latest best practices such as PMBoK and LEAN Construction and recent PMI Brightline 10 Guiding Principles. The Quality Manager works very closely with a CPMP to manage the quality of a construction project. As part of the CPMP Framework which is based on PMBoK, the above principles are used to:
- Adopt a CQM Philosophy and Strategy for CQM Implementation
- Show Leadership to Integrate Quality with a CQM Framework with a Quality Excellence Culture rather than forced management
- Have a Robust Plan with flexibilities to Customize
- Dedicate the appropriate CQM Assets and Resources
- Promote Quality Team Engagement and advocate PMO for CQM for multidisciplinary cross-business cooperation
- Listen to Stakeholders with Insight for customers and competitors,
- Apply CQM as defined processes, but keep them LEAN and Simple
- Improve Processes with collaborative problem-solving and collective decision-making
- Value CQM Training with Pairing, Coach with Shadowing, Drive-out Fear, Blame-Game, and Allow for Experimenting based on a Fail Fast to Learn Fast Mentality
- Share Knowledge, Recognize Efforts, and Celebrate Good Teamwork
TQM Quality Control Tools and Techniques are widely used in CQM and will be discussed as part of CQM Control section.






