What are the Best Quality KPIs? | Scilife
When it comes to quality management, nothing should be left to guesswork. In regulated industries, progress is often measured through quality-specific Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) known as Quality KPIs.
So, what are Quality KPIs?
Key Performance Indicators are a type of business performance metric. Setting KPIs helps you quantify what you want to achieve by when, so they’re really useful to see if you’re on track to meet your goals. In the case of Quality KPIs, these metrics are simply related to quality issues.
No matter what type of KPI you’ll choose to monitor, every KPI must follow a set structure to be a useful performance tool:
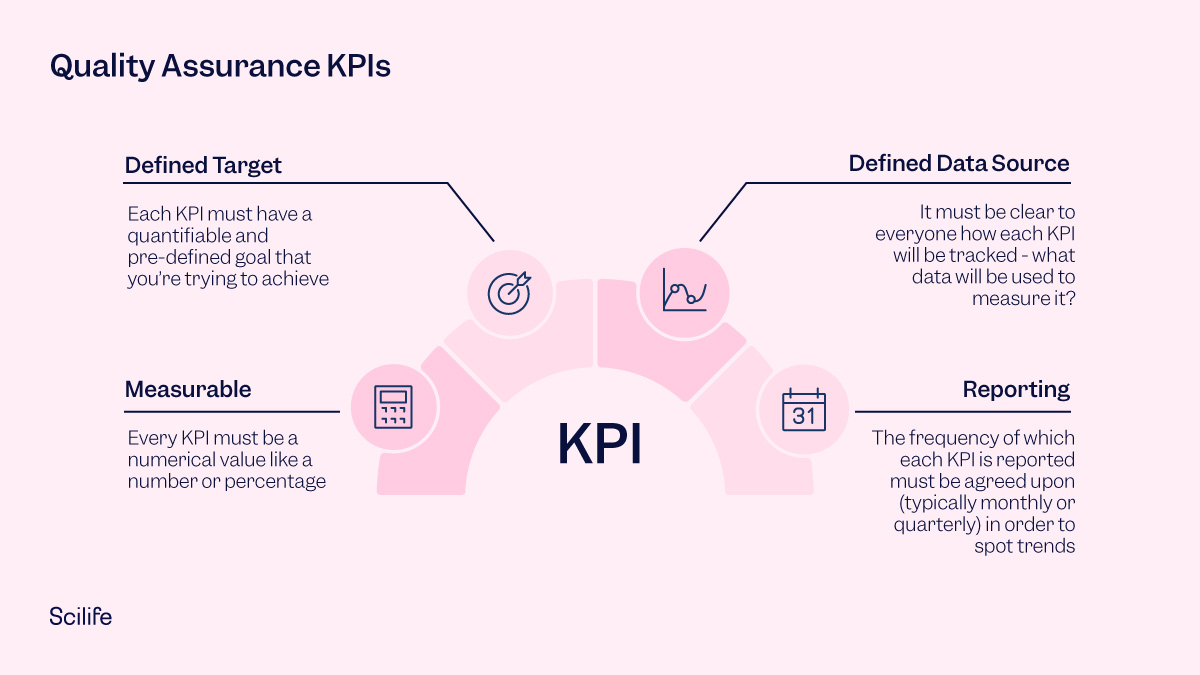
Before you choose which Quality KPIs to track
How do you know which Quality KPIs will drive positive change in your business? Which Quality KPIs are unmissable?
Although we’d love to name every single essential quality KPI for your business, the truth is that it depends on your company, your industry, your product, and so on and so forth – one size does not fit all. However, despite specific Quality KPIs being unique to each and every company, we can help you identify five broad areas of ‘business performance’ for which you could (and should) find measurement indicators.
Keep in mind that being aware of and working towards quality KPIs is everyone’s responsibility within a company, not just the quality department. It helps to involve your whole team when deciding upon and setting quality KPIs in the first place (read more about that on our blog here) so that only the most useful quality KPIs are tracked, rather than trying to track everything which is often counterproductive.

Do you want to take all this information with you?

Picking the best Quality KPIs
To ensure you’re tracking performance broadly enough across any business in the life sciences space, focus on the following 5 areas and pick KPIs that directly correlate to each:
1. Risk
Risk is an (if not the most) important area to monitor carefully in regulated industries like the life sciences. To analyze how well risk management activities are performing, tracking any of the following quality KPIs would be useful:
-
- Number of overdue training or required audit actions
- Overall audit score and risk level findings (both internal and external)
- Number of outstanding compliance issues/risks
- Number of overdue risk assessments
- Number of recent changes (the number of potential risks goes up when the complexity of the product or the number of process steps of the product increases. Product changes are a frequent culprit of quality issues.)
Scilife has a dedicated Risk Management module that makes risk assessment fast and efficient within your organization. These Risk Assessments can be linked to Scilife’s innovative KPI tracking module where managers can monitor their chosen quality KPIs in real-time and so are able to immediately observe potential risks across their organization.
2. Quality Response
A clear barometer of any crucial issues and future business success, strive to track KPIs that evaluate your customers, and how your team is handling them. After all, business reputation and loyalty are entirely dependent on superior customer service.
How do you find out if your customers are satisfied, if they would use your products again, and if they would recommend your service? Typically, through direct customer evaluation tools like a satisfaction survey (with quick, objective, and concise questions), or you can gather information from the search platforms that do this using tools like Net Promoter Score.
Examples of quality KPIs to provide a good idea of customer retention include:
-
- Customer satisfaction scores (e.g. Net Promoter Score (NPS))
- Customer churn rate
- Product quality complaint rate / Number of customer complaints
- Number of overdue issues
- Time to solve issues
- Time to respond
- Quality of communication
- Solution effectiveness
3. Cost of Quality
Finance-related quality KPIs allow you to estimate the financial impacts of your processes and help determine budgets and strategies for upcoming years.
Here are the metrics that can be analyzed:
3.a Cost of Poor Quality (CoPQ)
This metric can be used to see the impact of poor quality. It puts a number on the total loss due to either internal or external quality issues. Unwanted overheads caused by poor systems, processes, or practices, can drastically reduce business profitability. CoPQ can be measured by these quality KPIs, among others:
-
- Number of incidents
- Percentage of defects or rework needed
- Number of nonconformities
- Right-first-time percentage
- Time spent in root cause analyses or to resolve issues
- Amount of ‘wasted’ product/time
3.b Cost of High Quality (CoHQ)
Similar KPIs can be used to measure CoHQ, however, in this case, you estimate the costs of trying to achieve excellence. Don’t forget that achieving high quality in your processes has a cost too. For example, reducing defect rate from 1% to 0.01% might be a cost-effective goal, but reducing the defect rate down to 0.001% might be too costly and won’t make sense for the quality stakeholders.
4. Productivity
Productivity is generally viewed as a human performance metric – how efficiently your employee or team is working. In actual fact, productivity is an area that points to how optimized your company is, and can highlight systems or processes that could do with streamlining – rather than singling out less hardworking individuals.
Productivity can be gauged through quality KPIs such as:
-
- Number of overdue audit findings/issues/training
- Speed of response to findings
- Number of completed training
- In manufacturing/operations: metrics such as Lot Acceptance Rate & Invalidated Out-Of-Specification Rate
KPIs that show the level of productivity help you determine which and how many resources are needed to perform processes, help you identify wastes that need to be avoided, and help you discover the amount of time that a process needs. This area of performance directly impacts budget reviews and delivery schedules, so it’s crucial to track KPIs that analyze it.
A good digital quality management system (eQMS) like Scilife plays a big role in improving productivity KPIs, as it enables your business to track and react to actions and changes rapidly.
5. Quality Culture
An often overlooked but essential area that makes or breaks a business is the health of its quality culture. What’s a quality culture? A working environment where individuals are engaged with and are implementing good quality practices in their day-to-day tasks. The concept can be quite subjective but is estimated through quality KPIs that usually signify engagement with quality, governance, risk, and compliance management. Quantifiable examples include:
-
-
Training scores
-
Percentage of policies read & understood
-
The time that is taken to resolve issues
-
Quality Awareness Metric
-
Number of change requests or
events
-
Improvement Acceptance Ratio
– How many business suggestions are actually analyzed and implemented? If ideas are discarded directly, it’s an indicator for less future contribution from employees.
-
Scilife helps you set, track, and act on Quality KPIs
Quality KPIs not only measure the health of your organization, they can drive positive changes in individual and team behavior, help build a thriving quality culture, and ultimately boost the quality compliance and success of your business in all aspects. All in all, the right Quality KPIs guide your organization along the journey of continuous improvement.
Scilife’s KPI module visualizes and breaks down all sorts of real-time performance metrics in one centralized space, so that you’re always aware of how well your company is managing quality or other processes.
Discover areas for immediate improvement with out-of-the-box key performance indicators, filter and drill-down into historic data, dive into detail with clickable graphs, export and download reports, and integrate Scilife with your own Business Intelligence tools if desired.
Scilife helps life science companies track QA KPIs!
Find out more about the KPIs module here.






